For working professionals
For fresh graduates
- Study abroad
More
- Executive Doctor of Business Administration from SSBM
- Doctorate in Business Administration by Edgewood College
- Doctorate of Business Administration (DBA) from ESGCI, Paris
- Doctor of Business Administration From Golden Gate University
- Doctor of Business Administration from Rushford Business School, Switzerland
- Post Graduate Certificate in Data Science & AI (Executive)
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data Analysis
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software Development
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial Excellence
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content Creation
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Human Resource Analytics Course from IIM-K
- Directorship & Board Advisory Certification
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- CSM® Certification Training
- CSPO® Certification Training
- PMP® Certification Training
- SAFe® 6.0 Product Owner Product Manager (POPM) Certification
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps
- Python Programming Course
- Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full Stack
- AWS Solutions Architect Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
- AWS Technical Essentials
- The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from Microsoft
1. Introduction
6. PyTorch
9. AI Tutorial
10. Airflow Tutorial
11. Android Studio
12. Android Tutorial
13. Animation CSS
16. Apex Tutorial
17. App Tutorial
18. Appium Tutorial
21. Armstrong Number
22. ASP Full Form
23. AutoCAD Tutorial
27. Belady's Anomaly
30. Bipartite Graph
35. Button CSS
39. Cobol Tutorial
46. CSS Border
47. CSS Colors
48. CSS Flexbox
49. CSS Float
51. CSS Full Form
52. CSS Gradient
53. CSS Margin
54. CSS nth Child
55. CSS Syntax
56. CSS Tables
57. CSS Tricks
58. CSS Variables
61. Dart Tutorial
63. DCL
65. DES Algorithm
83. Dot Net Tutorial
86. ES6 Tutorial
91. Flutter Basics
92. Flutter Tutorial
95. Golang Tutorial
96. Graphql Tutorial
100. Hive Tutorial
103. Install Bootstrap
107. Install SASS
109. IPv 4 address
110. JCL Programming
111. JQ Tutorial
112. JSON Tutorial
113. JSP Tutorial
114. Junit Tutorial
115. Kadanes Algorithm
116. Kafka Tutorial
117. Knapsack Problem
118. Kth Smallest Element
119. Laravel Tutorial
122. Linear Gradient CSS
129. Memory Hierarchy
133. Mockito tutorial
134. Modem vs Router
135. Mulesoft Tutorial
136. Network Devices
138. Next JS Tutorial
139. Nginx Tutorial
141. Octal to Decimal
142. OLAP Operations
143. Opacity CSS
144. OSI Model
145. CSS Overflow
146. Padding in CSS
148. Perl scripting
149. Phases of Compiler
150. Placeholder CSS
153. Powershell Tutorial
158. Pyspark Tutorial
161. Quality of Service
162. R Language Tutorial
164. RabbitMQ Tutorial
165. Redis Tutorial
166. Redux in React
167. Regex Tutorial
170. Routing Protocols
171. Ruby On Rails
172. Ruby tutorial
173. Scala Tutorial
175. Shadow CSS
178. Snowflake Tutorial
179. Socket Programming
180. Solidity Tutorial
181. SonarQube in Java
182. Spark Tutorial
189. TCP 3 Way Handshake
190. TensorFlow Tutorial
191. Threaded Binary Tree
196. Types of Queue
197. TypeScript Tutorial
198. UDP Protocol
202. Verilog Tutorial
204. Void Pointer
205. Vue JS Tutorial
206. Weak Entity Set
207. What is Bandwidth?
208. What is Big Data
209. Checksum
211. What is Ethernet
214. What is ROM?
216. WPF Tutorial
217. Wireshark Tutorial
218. XML Tutorial
Kth Smallest Element
Introduction
In the realm of computer science and data analysis, finding the Kth smallest element in an array or data structure is a common problem with numerous applications. This task involves identifying the Kth smallest item from a collection of elements. Whether you're working with arrays, binary search trees, or unsorted arrays, there are several algorithms that can efficiently solve this problem. In this article, we will delve into various approaches to find the Kth smallest element and explore real-life examples to understand their applications better.
Overview
The Kth smallest element problem arises in various scenarios, such as finding the Kth smallest salary in a company's employee database, identifying the Kth lowest temperature in a weather dataset, or even ranking students based on their scores in an exam. The problem extends to different data structures, including arrays and binary search trees (BSTs), and can be approached using various algorithms.
Various Approaches to Find the Kth Smallest Element
Approach 1: Sorting the Array
Sorting the array is one of the simplest ways to find the Kth smallest element. The idea is to sort the entire array in ascending order, and then we can directly access the Kth element from the sorted array.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Sort the Array: We begin by sorting the given array in ascending order. Python provides built-in functions like sorted() and array methods like sort() to achieve this. Let's consider an example:
Example: Finding the 3rd smallest number in an array [9, 5, 7, 2, 3]
# Python code to sort the array and find the Kth smallest element
def find_kth_smallest(arr, k):
sorted_arr = sorted(arr) # Sorting the array
return sorted_arr[k - 1] # Accessing the Kth smallest element (index is k - 1)
# Test the function
arr = [9, 5, 7, 2, 3]
k = 3
result = find_kth_smallest(arr, k)
print(f"The {k}th smallest element is: {result}")
Output:
The function find_kth_smallest takes an array arr and an integer k as input. It first sorts the array arr in ascending order using the sorted() function, and then it returns the Kth smallest element by accessing the element at index k - 1 from the sorted array.
In this example, the input array is [9, 5, 7, 2, 3], and we want to find the 3rd smallest element. After sorting the array to [2, 3, 5, 7, 9], we access the element at index 3 - 1 = 2, which is 5, hence the output.
Advantages:
- Simple and easy to implement
- Works for both arrays and other data structures
- Suitable for small-sized datasets
Disadvantages:
- The time complexity of sorting the entire array can be high, O(n log n) in general, which might not be efficient for large datasets.
- Sorting modifies the original array, which may not be desirable in some scenarios.
Applications:
Sorting the array to find the Kth smallest element has applications in various domains:
- Statistics: Finding percentiles or quartiles in datasets
- Data Analysis: Identifying key data points in sorted datasets
- Ranking Systems: Determining the Kth rank in sorted rankings, such as sports rankings or employee performance evaluations.
Sorting the array is a straightforward approach to finding the Kth smallest element, suitable for smaller datasets or scenarios where simplicity is prioritized over efficiency. However, for larger datasets, other algorithms like Min Heap or QuickSort might be preferred due to their better time complexity. Understanding this basic approach helps build a strong foundation for exploring more advanced techniques in finding the Kth smallest element in various data structures.
Approach 2: Using Min Heap
A Min Heap is a binary tree data structure where the parent nodes are smaller than their children. By utilizing a Min Heap, we can efficiently find the Kth smallest element without the need to sort the entire array. Python provides the heapq module that allows us to create a Min Heap. Let's explore how this approach works with an example.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
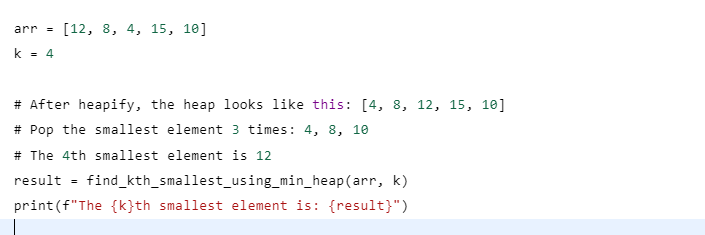
Example: Finding the 4th smallest number in an array [12, 8, 4, 15, 10]
- Create a Min Heap:
We start by creating a Min Heap from the given array. Python's heapq module provides functions like heapify() and heappush() to create and modify heaps.
- Pop the Smallest Element Four Times
- We pop the smallest element from the Min Heap four times to get the 4th smallest element.
- First pop: 4 is the smallest element
- Second pop: 8 is the smallest element
- Third pop: 10 is the smallest element
- Fourth pop: 12 is the smallest element
- Result: The 4th smallest element is 15
Python Code:
import heapq
def find_kth_smallest_using_min_heap(arr, k):
# Create a Min Heap
heapq.heapify(arr)
# Pop the smallest element k-1 times
for _ in range(k-1):
heapq.heappop(arr)
# The kth smallest element is at the top of the heap
return heapq.heappop(arr)
# Test the function
arr = [12, 8, 4, 15, 10]
k = 4
result = find_kth_smallest_using_min_heap(arr, k)
print(f"The {k}th smallest element is: {result}")
Provided input:
Output:
Advantages:
- The time complexity of building a Min Heap is O(n), and popping the smallest element takes O(k log n), making it efficient for finding the Kth smallest element.
- Does not require sorting the entire array
Disadvantages:
- The heap data structure consumes additional memory.
Applications:
Finding the Kth smallest element is crucial in various applications like priority queues, k-th order statistics, and top-k elements in large datasets.
Using a Min Heap approach is particularly useful when dealing with large datasets where sorting the entire array might be computationally expensive. Python's heapq module enables us to solve the Kth smallest element problem with excellent time complexity.
Approach 3: Using Max Heap
In this approach, we will use a Max Heap to find the Kth smallest element in the array. Unlike the Min Heap, a Max Heap is a binary tree data structure where the parent nodes are greater than their children. We will still use Python's heapq module to create and manipulate the Max Heap. We will walk you through the steps using an example.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Example: Finding the 2nd smallest number in an array [25, 18, 30, 14, 20]
- Create a Max Heap: We start by creating a Max Heap from the given array.
- Pop the Largest Element
We pop the largest element (root of the Max Heap) once, which removes it from the heap. We repeat this step k-1 times to get the Kth smallest element.
First pop: The largest element 30 is removed from the Max Heap.
- Result: The 2nd smallest element is 25.
Python Code:
import heapq
def find_kth_smallest_using_max_heap(arr, k):
# Convert the elements of the array to their negative values
# This will create a Max Heap from the Min Heap functions
max_heap = [-x for x in arr]
# Create the Max Heap from the modified array
heapq.heapify(max_heap)
# Pop the largest element (k-1) times
for _ in range(k-1):
heapq.heappop(max_heap)
# The kth smallest element is at the top of the Max Heap
return -heapq.heappop(max_heap)
# Test the function
arr = [25, 18, 30, 14, 20]
k = 2
result = find_kth_smallest_using_max_heap(arr, k)
print(f"The {k}nd smallest element is: {result}")
Output:
The Kth smallest element is at the top of the Max Heap. Since the elements were initially converted to negative values, the function returns the negation of the top element to get the actual Kth smallest element. In this example, the input array is [25, 18, 30, 14, 20], and we want to find the 2nd smallest element. The function correctly returns 25 as the output.
Advantages:
- Similar to the Min Heap approach, building a Max Heap has a time complexity of O(n), and popping the largest element takes O(k log n), making it efficient for finding the Kth smallest element.
- Does not require sorting the entire array
Disadvantages:
As with the Min Heap approach, the heap data structure consumes additional memory.
Applications:
- Finding the Kth smallest element using a Max Heap has similar applications to the Min Heap approach, such as priority queues, k-th order statistics, and top-k elements in large datasets.
Using a Max Heap is another efficient way to find the Kth smallest element in an array without sorting the entire array. By converting elements to their negative values, we can transform the Min Heap functions into Max Heap functions, making the approach easy to implement and understand.
Approach 4: Using QuickSort
QuickSort, a popular sorting algorithm, can be adapted to find the Kth smallest element efficiently. The algorithm works by selecting a pivot element, partitioning the array around the pivot, and then recursively performing the same operation on the left and right subarrays based on the pivot's position. Python's built-in sorted() function uses the QuickSort algorithm. Let's explore how this approach works with an example.
Step-by-Step Explanation:
Example: Finding the 5th smallest number in an array [35, 27, 40, 32, 38]
- Select the Pivot: We start by selecting a pivot element. In this example, let's choose 35 as the pivot.
- Partition the Array: We partition the array into three subarrays: elements smaller than the pivot, elements equal to the pivot, and elements greater than the pivot.
- Continue with Left Subarray: Since the left subarray has two elements, we can directly identify the 5th smallest element without further partitioning.
- Result: The 5th smallest element is 32.
Python Code:
def find_kth_smallest_using_quicksort(arr, k):
if len(arr) == 1:
return arr[0]
pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
if k <= len(left):
return find_kth_smallest_using_quicksort(left, k)
elif k <= len(left) + len(middle):
return middle[0]
else:
return find_kth_smallest_using_quicksort(right, k - len(left) - len(middle))
# Test the function
arr = [35, 27, 40, 32, 38]
k = 5
result = find_kth_smallest_using_quicksort(arr, k)
print(f"The {k}th smallest element is: {result}")
Advantages:
- QuickSort has an average-case time complexity of O(n log n) and performs well for large datasets.
- It does not require creating a heap or sorting the entire array, making it more memory-efficient compared to some other approaches.
Disadvantages:
- In the worst-case scenario, QuickSort's time complexity can be O(n^2), which is not desirable for very large arrays.
- QuickSort is not a stable sorting algorithm, meaning it may change the relative order of equal elements.
Applications
- QuickSort is widely used in various applications that require efficient sorting, such as database indexing, language interpreters, and file system directories.
Conclusion
The search for the Kth smallest element is a fundamental problem in computer science with various practical applications. Depending on the data structure and the efficiency requirements, we can use different algorithms to find the Kth smallest element. We explored five approaches, including sorting the array, using Min Heap, Max Heap, QuickSort, and maintaining an ordered map with frequencies. Each approach has its advantages and can be tailored to specific scenarios.
By employing these algorithms, we can efficiently identify the Kth smallest element in arrays or datasets, enabling us to solve a wide range of real-life problems, such as ranking data, finding extreme values, and selecting key items from a collection.
FAQs
- How can I efficiently find the Kth smallest element in a large dataset?
For large datasets, using a Min Heap or QuickSort-based approach can be more efficient than sorting the entire array or using a Max Heap. Min Heap helps find the Kth smallest element in O(k log n) time, while QuickSort has an average-case time complexity of O(n log n). Both methods avoid the overhead of sorting the entire dataset and are memory-efficient.
- How do I handle duplicates when finding the Kth smallest element?
When handling duplicates, the approach using an ordered map and element frequencies is effective. By maintaining an ordered map (e.g., Python's collections.Counter), we can efficiently keep track of element occurrences and iterate through the map to find the Kth smallest element without sorting the entire array. This approach considers the frequency of elements and ensures accurate results even with duplicates.
- How can I find the Kth smallest element in a Binary Search Tree (BST)?
To find the Kth smallest element in a BST, an in-order traversal of the tree can be employed. In an in-order traversal, we visit the left subtree first, followed by the root node, and then the right subtree. By counting the number of nodes visited during the traversal, we can identify the Kth smallest element when it is encountered. The in-order traversal has a time complexity of O(log n + k), where n is the number of nodes in the BST.

Author|900 articles published


upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 9 AM to 12 AM (midnight)
Indian Nationals
1800 210 2020
Foreign Nationals
+918068792934
Disclaimer
1.The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
2.The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not provide any a.