For working professionals
For fresh graduates
- Study abroad
More
- Executive Doctor of Business Administration from SSBM
- Doctorate in Business Administration by Edgewood College
- Doctorate of Business Administration (DBA) from ESGCI, Paris
- Doctor of Business Administration From Golden Gate University
- Doctor of Business Administration from Rushford Business School, Switzerland
- Post Graduate Certificate in Data Science & AI (Executive)
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data Analysis
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software Development
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial Excellence
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content Creation
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Human Resource Analytics Course from IIM-K
- Directorship & Board Advisory Certification
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- CSM® Certification Training
- CSPO® Certification Training
- PMP® Certification Training
- SAFe® 6.0 Product Owner Product Manager (POPM) Certification
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps
- Python Programming Course
- Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full Stack
- AWS Solutions Architect Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
- AWS Technical Essentials
- The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from Microsoft
1. Introduction
6. PyTorch
9. AI Tutorial
10. Airflow Tutorial
11. Android Studio
12. Android Tutorial
13. Animation CSS
16. Apex Tutorial
17. App Tutorial
18. Appium Tutorial
21. Armstrong Number
22. ASP Full Form
23. AutoCAD Tutorial
27. Belady's Anomaly
30. Bipartite Graph
35. Button CSS
39. Cobol Tutorial
46. CSS Border
47. CSS Colors
48. CSS Flexbox
49. CSS Float
51. CSS Full Form
52. CSS Gradient
53. CSS Margin
54. CSS nth Child
55. CSS Syntax
56. CSS Tables
57. CSS Tricks
58. CSS Variables
61. Dart Tutorial
63. DCL
65. DES Algorithm
83. Dot Net Tutorial
86. ES6 Tutorial
91. Flutter Basics
92. Flutter Tutorial
95. Golang Tutorial
96. Graphql Tutorial
100. Hive Tutorial
103. Install Bootstrap
107. Install SASS
109. IPv 4 address
110. JCL Programming
111. JQ Tutorial
112. JSON Tutorial
113. JSP Tutorial
114. Junit Tutorial
115. Kadanes Algorithm
116. Kafka Tutorial
117. Knapsack Problem
118. Kth Smallest Element
119. Laravel Tutorial
122. Linear Gradient CSS
129. Memory Hierarchy
133. Mockito tutorial
134. Modem vs Router
135. Mulesoft Tutorial
136. Network Devices
138. Next JS Tutorial
139. Nginx Tutorial
141. Octal to Decimal
142. OLAP Operations
143. Opacity CSS
144. OSI Model
145. CSS Overflow
146. Padding in CSS
148. Perl scripting
149. Phases of Compiler
150. Placeholder CSS
153. Powershell Tutorial
158. Pyspark Tutorial
161. Quality of Service
162. R Language Tutorial
164. RabbitMQ Tutorial
165. Redis Tutorial
166. Redux in React
167. Regex Tutorial
170. Routing Protocols
171. Ruby On Rails
172. Ruby tutorial
173. Scala Tutorial
175. Shadow CSS
178. Snowflake Tutorial
179. Socket Programming
180. Solidity Tutorial
181. SonarQube in Java
182. Spark Tutorial
189. TCP 3 Way Handshake
190. TensorFlow Tutorial
191. Threaded Binary Tree
196. Types of Queue
197. TypeScript Tutorial
198. UDP Protocol
202. Verilog Tutorial
204. Void Pointer
205. Vue JS Tutorial
206. Weak Entity Set
207. What is Bandwidth?
208. What is Big Data
209. Checksum
211. What is Ethernet
214. What is ROM?
216. WPF Tutorial
217. Wireshark Tutorial
218. XML Tutorial
Change Font Color Using CSS
Introduction
One of the fun parts of designing a webpage is deciding how it will look. The color of your text plays a huge part in this. It can set the mood of your page and make it easier for visitors to read your content. So, how do you change the font color on your webpage? The answer is CSS or Cascading Style Sheets. Yes, you can change the font color using CSS.
CSS is a coding language that styles HTML content. It's like the paintbrush that adds color to your raw HTML sketches. With CSS, you can easily adjust the font color of your text, whether it's for a single word, a paragraph, or an entire webpage.
In this guide, we'll take you through the steps to change the font color using CSS. After going through this, you can customize your web pages even more and make them stand out.
Overview
This guide will explore how to change font color using CSS online on your webpage. We'll refer to trustworthy resources like the CSS MDN (Mozilla Developer Network) to understand how to change the text color the CSS MDN provides.
HTML is the structure of your webpage; with it, you can also change text color in HTML, which allows it without the need to delve into CSS. However, CSS provides much more control and options over the style. We'll look into style=font color, a common syntax used to define text color, along with other text style CSS properties.
The power of CSS doesn't stop at colors. You can also make CSS text bold, among other things, to further highlight important parts of your text.
We'll also explore CSS colors in general. This will allow you to understand not just how to change color but also how to pick the perfect shade for your text.
In a nutshell, this guide will cover all you need to enhance your text's appearance on the web.
The Basic Structure of An HTML File
HTML, which stands for Hyper Text Markup Language, is the standard language for creating webpages. It uses tags, which are surrounded by angle brackets < >, to structure the content on the webpage.
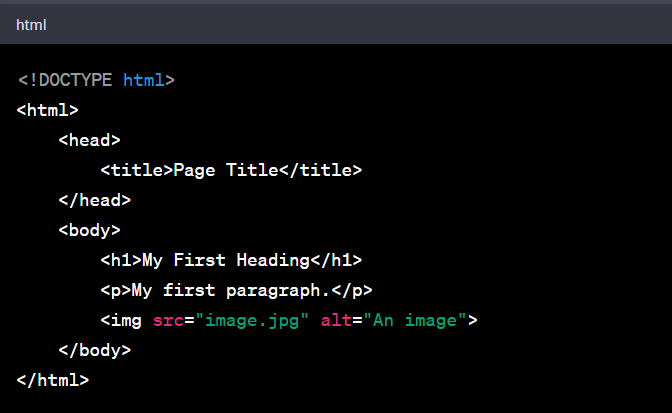
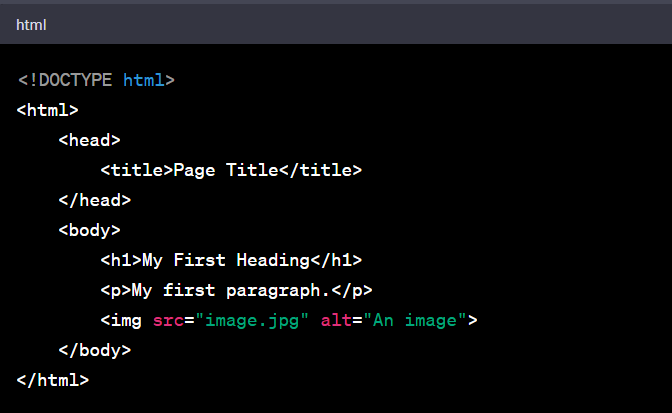
Here's the basic structure of an HTML document:
Let's break down the elements of this file:
- <!DOCTYPE html>: This is the document type declaration, and it must be the very first thing in your HTML document before the <html> tag. It's information to the web browser about what version of HTML the page is written in.
- <html>: This tag is the root of an HTML document. Everything inside it makes up the whole webpage.
- <head>: The head element contains meta-information about the HTML document that isn't displayed on the webpage itself. This includes the title of the page, character set, styles, scripts, and other meta information.
- <title>: This tag is found within the head and sets the title of the webpage, which is displayed in the browser tab.
- <body>: This tag contains the content that is displayed to web users when they visit your page. It can contain text, images, audio, video, etc.
- <h1>: This is a heading tag. HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags. <h1> defines the most important heading, and <h6> defines the least important.
- <p>: This is a paragraph tag. It defines a paragraph of text.
- <img>: This tag is used to embed an image in the HTML document. The src attribute specifies the path to the image file. The alt attribute provides alternative text for browsers that cannot display the image.
You can easily test the above HTML code by creating a new .html file on your computer, pasting the code into it, and opening it in a web browser. You will see a webpage with the title "Page Title", a heading "My First Heading", a paragraph "My first paragraph.", and an image (if there's an image named "image.jpg" in the same directory as your HTML file).
Setting Up an HTML File
To set up an HTML file, you need a text editor and a web browser. Here are the steps you have to follow:
- Open a text editor: This can be a basic editor like Notepad (Windows) or TextEdit (Mac), or a more advanced code editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom.
- Create a new file: You can usually do this by going to "File" > "New" in your text editor.
- Write or paste in your HTML code: You can start with the basic HTML structure provided earlier:
- Save the file: Go to "File" > "Save As". Make sure to save the file with a .html extension, like "index.html" or "myfirstpage.html". It's common to name the main page of a website "index.html".
- Open the file in a web browser: You can do this by double-clicking on the file or right-clicking and choosing "Open with" and selecting a web browser. The HTML file will be rendered by the browser, and you will see the webpage as it will appear to users.
Learning How To Change Text Color In CSS
In CSS, the color property changes the color of the text. The color can be specified in three ways:
- Using a color name, like "red"
- Using a HEX value, like "#ff0000"
- Using an RGB value, like "rgb(255,0,0)"
All modern browsers support 140 color names that you can use in your CSS files.
The default text color for a page is defined in the body selector.
Changing the text color in CSS is simple and can be done in a few steps. Here's how to do it:
- Identify the HTML Element: First, you need to know the HTML element you want to change the color for. This could be an <h1>, <p>, or any other HTML element.
- Style the HTML Element in CSS: Now, you need to select this element in your CSS. There, write the name of the element, followed by {}. Inside these brackets, you'll put your styling.
- Change the Color: Inside the brackets, write color: followed by the color you want. The color can be called by name (like red or blue), a hex value (like #ff0000 for red), or an RGB value (like rgb(255, 0, 0) for red).
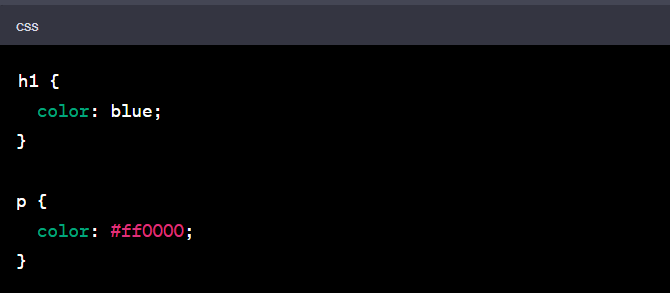
In this example, the <h1> will show in blue, and the paragraph will be red.
Remember
CSS gives you a lot of flexibility when choosing colors. CSS has a broad CSS color spectrum, where you can choose from named colors, hex values, or RGB values. You can even use HSL values (hue, saturation, and lightness) or RGBA values (red, green, blue, and alpha) for transparent colors. This wide range gives you the freedom to choose exactly the color you want.
Using Hexadecimal Values to Change Text Colors in CSS
Besides color keywords, CSS also supports hexadecimal (or hex) values for colors. Hex values are six-digit codes that represent red, green, and blue color values. They always start with a '#'.
Here's how you can use hex values to change text color in CSS:
Example 1:
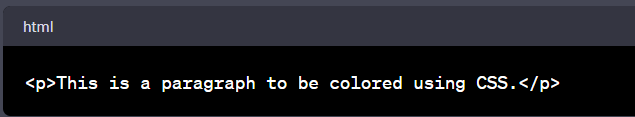
- HTML Element: Let's start with a paragraph (<p> tag).
- Apply the Hex Value: In CSS, select the HTML element and apply the hex value in the color property.
In this example, the paragraph text will be red because '#FF0000' represents that color.
Using RGBA Color Values To Change Text Color In CSS
CSS also supports RGBA color values, which are great when you need to change not just the color but also the opacity of your text. The RGBA stands for Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha (transparency). Each of these values can range from 0 to 255, with Alpha also accepting values between 0 (completely transparent) and 1 (completely opaque).
Here's how you can use RGBA color values to change text color in CSS:
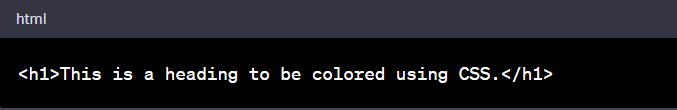
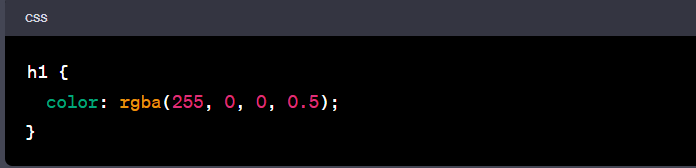
- Choose the HTML Element: Let's select a heading (<h1> tag) for this example.
- Apply the RGBA Value: In CSS, select the HTML element and apply the RGBA value in the color property.
In this example, the heading text will appear in semi-transparent red. The values 255, 0, 0 correspond to red, and 0.5 sets the transparency level to 50%.
Conclusion
We've now covered various ways to change the color of your text using CSS. Whether you're choosing from the color keywords, using hexadecimal values for precise control, or playing around with RGBA values for color and transparency, CSS offers you a world of options.
Also, CSS doesn't stop at colors. From bolding text to styling your fonts, you can explore so much more.
Even if you're not using CSS, HTML allows for quick and simple changes. With the style attribute, you can set your text color directly in your HTML tags.
Mastering these skills will not only help your web pages look better, but they'll also give you more control over the user experience on your site.
FAQs
- What is the default font color in CSS?
The default font color in CSS, if not specified, is usually black. However, it can depend on the browser or user settings.
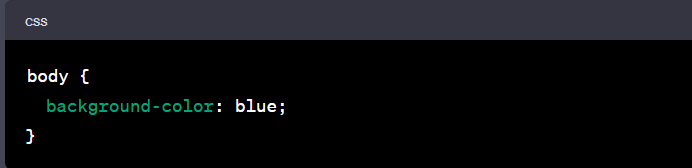
- How can I change the background color using CSS?
To change the background color using CSS, use the 'background-color' property. For example, to make the background blue, you have to use:
- How do I change the color of a hyperlink in CSS?
To change the color of a hyperlink, you target the 'a' tag in your CSS. For example, to make the link color red, you have to use:
- What is the difference between 'color' and 'background-color' in CSS?
'Color' in CSS refers to the color of the text, while 'background-color' refers to the color behind the text or the background of an element.
- How can I change the font color for a specific section of my webpage?
To change the font color for a specific section, you can assign a class or id to that section in your HTML. Then, target that class or id in your CSS to apply the color.
- How can I change the font color when the mouse hovers over the text?
You can use the ':hover' selector in CSS. For example, to change the color to blue when hovering over a link, you have to use:
- How can I change the color of a list bullet in CSS?
To change the color of a list bullet, you can use the 'list-style' property in combination with 'color'. This will change both the bullet color and the text color.

Author|900 articles published


upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 9 AM to 12 AM (midnight)
Indian Nationals
1800 210 2020
Foreign Nationals
+918068792934
Disclaimer
1.The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
2.The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not provide any a.