Introduction
Love building with React, but struggle with slow initial page loads or poor SEO? That's the exact problem Next.js was built to solve.
So, what is Next.js? It's a powerful framework that supercharges your React apps with features like Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and static site generation. This means your websites load faster, perform better, and are loved by search engines.
This Next.js Tutorial is your complete guide to getting started. We'll take you from the basic setup and file-based routing to building full-stack applications with ease. Ready to build faster, more powerful web apps? Let's dive in.
Go beyond just writing code. upGrad’s Software Engineering courses teach you how to build powerful solutions and land the high-impact tech career you've been looking for.
Overview
Next.js is an open-source React front-end development web framework that makes building websites and apps easy. Known for its fast performance and efficient code splitting, it has become a favorite among developers.
There are countless examples of Next.js websites. These range from basic web pages to intricate e-commerce sites, showcasing the adaptability and power of this framework. Many renowned companies and individual developers have utilized Next.js to enhance the user experience of their sites.
This Next.js tutorial will help you build your first Next.js project. This web framework offers the tools and features you need for the task.
Also Read: Web Designers vs Web Developers: Difference Between Web Designers and Web Developers
What is Next.js?
A powerful framework for React
At its core, Next.js is a framework for building server-rendered React applications. React allows you to craft interactive user interfaces. But with Next.js, you can supercharge these interfaces, making them even more efficient and user-friendly.
Server-Side Rendering (SSR) Magic
One of the standout features of Next.js is its server-side rendering. With SSR, your web pages can load content before they reach the user's browser. This means faster page loads and a better experience for your audience.
Flexibility and Scalability
Next.js is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It offers flexibility. Whether you're creating a small personal blog or a large-scale e-commerce platform, Next.js scales with your needs, ensuring a smooth development process.
Want to fast-track your tech career? Our Software Engineering Courses equip you with the skills to innovate, lead, and seize the next big opportunity.
Why Next.js?
Choosing the right tool for your project is vital when starting web development. With many options available, why should you pick Next.js? Let's explore the reasons.
- Enhanced Performance with Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Consider two similar e-commerce sites. One built with a regular JavaScript framework and another with Next.js. The Next.js site loads product pages almost instantly, while the other takes a few moments. That's the power of SSR, providing a competitive edge in user experience.
- Automatic Code Splitting
Think about reading a book. Instead of lugging around a 1000-page novel, wouldn't it be easier to carry just the chapter you're reading? Next.js does this with your code. It only loads what's needed, ensuring faster page loads.
- Easy Data Fetching
Imagine a news website. With Next.js, as soon as you click on a news article, it fetches the latest data, ensuring you always get real-time updates.
Also Read: 10 Practical Applications of JavaScript And Career Tips
- Seamless Transition between Pages
Browsing a portfolio site is like flipping through an artist's sketchbook. With Next.js, moving between projects feels fluid, almost like turning pages, thanks to its pre-rendering feature.
Installing and Configuring Next.js
Starting with Next.js is a simple process. You'll have a development environment ready to bring your web ideas to life in just a few steps.
System Prerequisites: Ensure you have the following installed on your computer:
- Node.js (10.13 or later)
- npm (Node Package Manager)
Creating a New Project:
Begin by setting up a new Next.js project. Open your terminal or command prompt and type:

Replace nextjs-tutorial with your desired project name.
Navigate to Your Project:
Once the setup is done, move to your project directory:

Run Your Project:
Now, let's see if everything's working as expected:

Upon entering this command, your app should start, and you can view it by going to http://localhost:3000 in your web browser.
Configuring for Custom Needs:
Next.js is designed to work out of the box, but you can tweak it. For custom configurations:
- Create a next.config.js file in your project root
- You can adjust various settings like custom Webpack configurations or environment variables within this file.
Adding Styles:
Next.js supports CSS and Sass. To use global styles:
- Create a styles directory
- Add .css or .scss files
- Import them in _app.js.
Consider using CSS modules for component-level styles by naming your style files ComponentName.module.css.
Also Read: 30 Front-End Developer Skills Every Developer Should Know in 2025!
Core Concepts and Components of Next.js Explained
The key concepts and components that set Next.js apart are:
- Pages: In Next.js, every file inside the pages directory becomes a route automatically. The component exported from a file like about.js is accessible at yourwebsite.com/about.
- API Routes: By placing a file inside the pages/api directory, you can craft an API endpoint. For instance, pages/api/hello.js responds to yourwebsite.com/api/hello.
- Static File Serving: For images, fonts, or other static assets, place them in the public directory. They're then served at the root level. So, an image at public/me.jpg can be viewed at yourwebsite.com/me.jpg.
- Dynamic Routing: Next.js supports file and folder naming as a form of dynamic routing. By naming a file [id].js, you're indicating that id is a variable, allowing for routes like yourwebsite.com/post/1.
- Built-in CSS Support: With Next.js, you can effortlessly add component-level styles using CSS modules or global styles.
- Head Component: SEO matters. The built-in Head component lets you modify the HTML head of a page. Whether you want to change the title, add meta tags, or insert styles/scripts, it’s all doable.
- Image Component: Next.js offers a built-in Image component optimized for enhanced performance. It handles tasks like lazy loading and reduces the need for external libraries.
- Environment Variables: Safekeeping sensitive data like API keys is vital. With Next.js, you can use environment variables, keeping your secrets secured while easily accessing them in your app.
Also Read: What Is REST API? Main Elements, Examples & Challenges
Achieving optimal performance isn’t just about the tools you use; it's also about how you use them. With Next.js, there are some best practices that can elevate your website or app to new heights.
- Utilize Static Generation: Whenever possible, pre-render pages at build time. This means faster page loads for users, as content gets served from a global content delivery network (CDN).
- Limit Use of Client-side Rendering: Rely on client-side rendering sparingly. It's best for content that changes constantly, like user dashboards. For everything else, prioritize static generation or server-side rendering.
- Image Optimization: Make the most of the built-in Image component. It automatically optimizes and resizes images based on the viewport, ensuring faster loads and less bandwidth usage.
- Lazy Load Non-essential Components: If certain components on your page aren’t immediately needed, consider lazy loading them. This means they’ll only load when necessary, speeding up initial page views.
- Split Large Bundles: Next.js does automatic code splitting, but you should also be mindful of creating lean components. Avoid bundling too much into one page or component.
- Minimize Third-Party Modules: External libraries and modules can slow things down. Only include what’s absolutely necessary, and always check the performance impact of third-party tools.
- Keep an Eye on API Calls: Limit the number of API calls made during server-side rendering. Each one can add to the time it takes for a page to be ready. Cache responses when feasible.
- Utilize Built-in Profiling: Next.js comes with a built-in React Profiler. It helps identify performance bottlenecks in your React components.
- Continuous Updates: Stay updated with the latest versions of Next.js, which usually brings performance enhancements and optimizations.
- Monitor with Next.js Analytics: This feature provides real-world performance data for your application. Use it to spot areas of your site or app that might need tweaking.
Also Read: 20+ Top Front-End Developer Tools in 2025: Uses, Benefits, and More
Create Your First Next.js Project
Creating your first Next.js project is exciting. Let's go through the step-by-step process to build a strong foundation.
- Setting Up: Before you start, make sure Node.js and npm are installed. If not, download and install them from the official Node.js website.
- Initiate Your Project: Open your terminal and type:
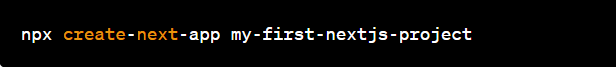
Replace my-first-nextjs-project with your chosen project name.
- Navigate and Run: Change to your project directory:
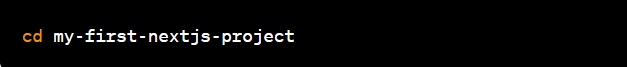
Now, launch your development server:
Your project is live! Visit http://localhost:3000 to see it in action
- Understand the Structure
Open your project in a code editor. The primary folders you’ll interact with are:
- pages: Where your main application components and routes live
- public: For static assets like images
- styles: For your global CSS
- Create a New Page: To add a new page, say "About", create an about.js file in the pages directory. Export a React component, and it'll be accessible at yourwebsite.com/about.
- Style Your Page: Next.js allows both global and modular CSS. For global styles, use the styles directory. Name your CSS file for component-specific styles as ComponentName.module.css and import it into your component.
- Add Dynamic Content: Leverage the power of server-side rendering. If you're fetching posts, you can use the getServerSideProps function within your page component to load data before rendering.
- Deploying Your Project: When you're ready to share your work with the world, deploy it. Popular options include Vercel, Netlify, and AWS Amplify. Choose one that fits your needs.
Also Read: Top Open Source Projects for Beginners
Advantages and Disadvantages of Next.js
Advantages | Disadvantages |
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Enables fast page loads and improved SEO. | Learning Curve: For beginners, especially those unfamiliar with React, there might be a steep learning curve. |
Static Site Generation (SSG): Build pages at run-time, offering even faster load times for certain pages. | Overhead: For simple projects, Next.js might introduce unnecessary complexity. |
Automatic Code Splitting: Loads only what’s required, optimizing performance. | Configuration Limitations: While it's designed for zero-config, custom setups can be tricky. |
Built-in CSS and Sass: There is no need for additional configurations to use CSS or Sass. | Server Restrictions: Some features, like SSR, require a Node.js server environment. |
API Routes: Easily create API endpoints, centralizing the backend and front end. | Larger Bundles: The built-in features can sometimes lead to bigger JavaScript bundles compared to more lightweight frameworks. |
Dynamic Import: Allows you to load modules and components on demand, improving performance. | Less Control: Opinionated structures may limit custom configurations for some developers. |
Optimized Image Component: Automatic image optimization to improve web performance. | Integration Challenges: While rare, some third-party packages might not be fully compatible without tweaks. |
Active Community: Benefits from an active community, ensuring regular updates, plugins, and solutions to common problems. | Migration Efforts: Moving an existing project to Next.js can demand significant rework and adjustment. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, this Next.js Tutorial has answered the fundamental question: what is Next.js? It’s more than just a framework; it's a powerful toolkit for building production-ready React applications.
You’ve seen how features like Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and file-based routing lead to faster, more SEO-friendly websites. The best way to master Next.js is to take what you've learned here and start building. Happy coding!
FAQs
1. How does Next.js handle data fetching?
Next.js provides built-in methods, like getStaticProps, getServerSideProps, and getStaticPaths, to fetch data for your pages. These methods allow for data fetching at build time, on each request, or for dynamic routes. What's the difference between Next.js and Create React App (CRA)?
2. What's the difference between Next.js and Create React App (CRA)?
Next.js and CRA are frameworks for building React applications. The former focuses on server-side rendering and static site generation, offering better SEO. The latter primarily set up a client-side rendered React application. How does Next.js fit into the Jamstack architecture?
3. How does Next.js fit into the Jamstack architecture?
Next.js aligns well with the Jamstack (JavaScript, APIs, and Markup) approach. Its ability to pre-render pages as static HTML fits the "markup" aspect, while its API routes and data fetching methods align with the "JavaScript and APIs" components of Jamstack. What databases work best with Next.js?
4. What databases work best with Next.js?
Next.js is database agnostic. You can integrate relational databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL or NoSQL ones like MongoDB with Next.js. The choice largely depends on the needs of your application.


-35c169da468a4cc481c6a8505a74826d.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)






%20(1)-d5498f0f972b4c99be680c2ee3b792d7.svg)












-d9bdeff6165f4eb1ba2adcebde78e961.svg)








-ae8d039bbd2a41318308f8d26b52ac8f.svg)











