Understanding the types of errors in C is essential for writing clean and efficient code. Errors can stop a program from running, crash it mid-execution, or produce wrong results. These errors fall into several categories: syntax, runtime, logical, linker, and preprocessor errors. Knowing how each one works helps you debug your code faster and write better programs.
In this article, you’ll learn about each error type with clear examples. We’ll explain how these errors occur, why they matter, and how you can fix or avoid them.
Explore our in-depth Software engineering courses to get a broader perspective.
How to Read an Error in C?
To address an error in our code, it is crucial to understand its cause and occurrence. When encountering an error, the compiler halts the compilation process if it detects a syntax error. The specific line of code responsible for the error is usually highlighted in such cases. The root cause of the error can often be identified on the highlighted line or in the code above it.
The syntax for error in C is -
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, world!")
return 0;
} |
In this example, a syntax error occurs due to the missing semicolon (;) at the end of the printf statement. The compiler would highlight the line and display an error message indicating the syntax error.
Pursue a Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps to prepare for the next big tech revolution!
Run-Time Error example :
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 5;
int b = 0;
int result;
result = a / b;
printf("Result: %d", result);
return 0;
} |
A run-time error occurs in this case because we attempt to divide an integer by zero. During program execution, a run-time error is detected, causing the program to terminate abruptly. The division by zero is not allowed and leads to undefined behaviour.
Logical Error example :
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int radius = 5;
double pi = 3.14;
double area;
area = pi * radius * radius;
printf("Area: %f", area);
return 0;
} |
Here, a logical error arises due to an incorrect formula for calculating the area of a circle. The formula should be pi * radius * radius, but the programmer mistakenly uses pi * radius instead. As a result, the program will produce incorrect output for the area.
Check out the Master of Design in User Experience program!
Types of Errors in C Programming
Here is a list of types of errors in c with examples -
Syntax Error in C
Syntax error in C occurs when the code violates the rules and structure of the programming language. These errors prevent the code from being compiled and executed. The compiler identifies syntax errors and displays error messages pointing to the specific line or lines where the error occurred.
If you are new to C programming, then you must explore the Features of C Language article.
Causes of Syntax Errors:
- Missing or incorrect punctuation marks: Forgetting to include semicolons (;) at the end of statements or using parentheses, brackets, or braces incorrectly.
- Mismatched parentheses, brackets, or braces: Failing to close or open parentheses, brackets, or braces properly can lead to syntax errors.
- Misspelt keywords or identifiers: Incorrectly typing keywords, variable names, or function names can result in syntax errors.
- Improper use of operators: Using operators incorrectly or placing them in the wrong order can cause syntax errors.
Examples -
Missing Semicolon -
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, world!")
return 0;
} |
In this example, a semicolon is missing at the end of the printf statement. The compiler will display an error message indicating the missing semicolon.
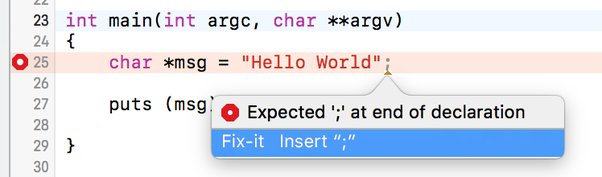
Mismatched Bracket:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
if (1 > 0) {
printf("True");
else {
printf("False");
}
return 0;
} |
In this example, there is a mismatched bracket in the if statement. The closing bracket for the if block is missing before the else statement. The compiler will detect this syntax error and provide an error message.
Runtime Error in C
Runtime errors in C, also known as exceptions or execution errors, occur during the execution of a program. Unlike syntax errors, runtime errors do not prevent the code from being compiled, but they cause the program to behave unexpectedly, crash, or produce incorrect output. Runtime errors are typically caused by invalid input, zero division, accessing out-of-bounds memory, or incompatible data types.
Causes of Runtime Errors:
- Poor Programming: Runtime errors can occur due to coding mistakes, memory leaks, or inadequate error handling.
- Aging/Damaged Hardware: Runtime errors can be caused by deteriorating or faulty hardware components.
- Software Interference: Conflicting or poorly performing software can trigger runtime errors in other programs.
- Virus/Malware Infections: Viruses and malware can disrupt software execution and lead to runtime errors.
Examples of Runtime Errors:
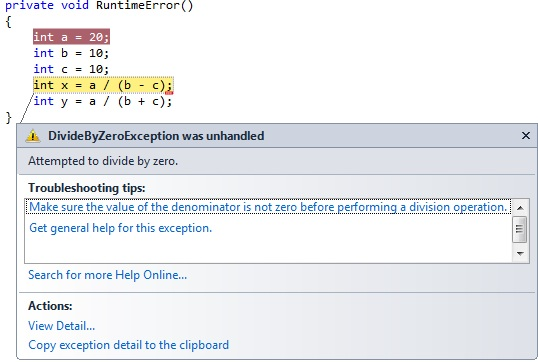
Division by Zero:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
int result;
result = a / b;
printf("Result: %d", result);
return 0;
} |
In this example, a runtime error occurs because we are attempting to divide an integer by zero. During program execution, a runtime error is detected, and the program terminates abruptly.
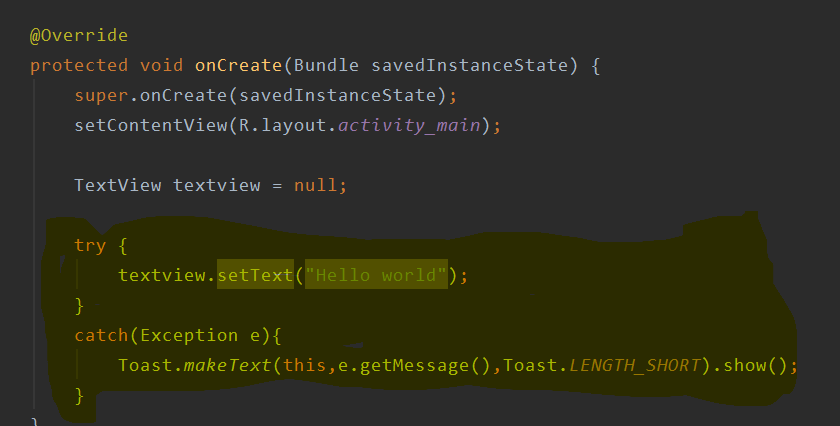
Null Pointer Dereference:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int* ptr = NULL;
*ptr = 10;
return 0;
} |
Must Read: 29 C Programming Projects in 2025 for All Levels [Source Code Included]
Logical Error in C
Logical error in C, also known as semantic errors, occur when the program runs without any syntax or runtime errors but produces incorrect or unexpected results. These errors are caused by flawed logic or incorrect algorithmic implementation in the code.
Unlike syntax or runtime errors, logical errors do not generate error messages or warnings from the compiler or runtime system. Detecting and fixing logical errors requires careful analysis of the code's logic and understanding of the intended behaviour.
Causes of Logical Errors:
- Incorrect Sequence: Wrong order of code execution leading to unexpected outcomes.
- Wrong Boolean Expression: Incorrect evaluation of conditions or incorrect use of Boolean expressions.
- Incorrect Data Type Usage: Using incompatible or incorrect data types for variables or operations.
- Missing Logic: Omission of necessary logic or checks in the code.
Examples of Logical Errors -
Incorrect Sequence:
a = 5
b = 3
c = a + b
print(c)
a = b
print(a) |
In this example, the sequence of statements is incorrect. The value of a is printed before it is updated to b, resulting in the output being 5 instead of 3.
Wrong Boolean Expression:
x = 10
y = 5
if x < y or x > y: # Incorrect Boolean expression
print("x is not equal to y")
else:
print("x is equal to y") |
In this example, the Boolean expression used in the if statement is incorrect. Instead of checking for equality between x and y, it checks for inequality. This leads to the incorrect output "x is not equal to y" even when x and y are equal.
Linker Errors
Linker errors occur during the linking phase of the program's compilation process. The linker resolves external references, combines multiple object files, and generates the final executable file. Linker errors occur when there are issues with linking the object files together to create the executable.
Causes of Linker Errors:
- Undefined Symbols: When the linker cannot find the definition of a referenced symbol (function, variable, or class) because it is not defined or implemented.
- Duplicate Definitions: When multiple source files have definitions for the same symbol, causing conflicts during the linking process.
- Missing Libraries or Dependencies: When required libraries or dependencies are not properly linked or included in the project.
- Incompatible Architectures or Platforms: Compatibility issues occur when object files or libraries are compiled for different architectures or platforms, are linked together.
Examples of Linker Errors
Undefined Symbol Error:
main.obj : error LNK2019: unresolved external symbol addNumbers referenced in function main |
In this example, the linker error indicates that the symbol addNumbers is referenced in the main function but is not defined or implemented in any object files. It suggests that the function addNumbers needs to be defined or adequately linked.
Duplicate Symbol Error:
first.obj : error LNK2005: _variableName already defined in second.obj |
This linker error occurs when the symbol _variableName is defined in both first.obj and second.obj. It indicates a conflict due to duplicate definitions and suggests resolving the issue by ensuring unique symbol names.
Preprocessor Errors
Preprocessor errors occur during the preprocessing phase of the compilation process, where the preprocessor directives are processed before the actual compilation begins. These errors are related to the preprocessing directives and can prevent the code from being properly processed and compiled.
Causes of Preprocessor Errors:
- Missing/incorrect directives: Errors due to missing or incorrect preprocessor directives like forgetting to include necessary headers or using incorrect syntax.
- Circular dependencies: Errors caused by circular dependencies among header files, leading to an infinite preprocessing loop.
- Macro-related issues: Errors arising from missing/incorrect macro definitions, improper macro expansions, or conflicts between macros.
- Conditional compilation issues: Errors resulting from improperly structured or evaluated conditional compilation directives like #ifdef, #ifndef, #if, etc., and mismatched/unbalanced directives.
Must Explore: History of C Language
Examples of Preprocessor Errors:
Missing Header File:
If a required header file is not included or the file path is incorrect, it can cause a preprocessor error. For example,
#include <stdio.h>
#include <invalid_header.h> |
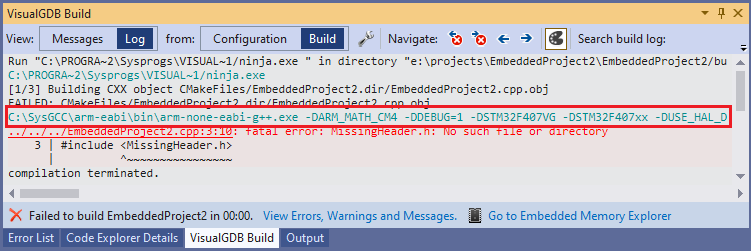
Circular Dependency:
When two header files include each other, it leads to a circular dependency and preprocessor error. For example,
#ifndef FILE1_H
#define FILE1_H
#include "file2.h"
#endif
#ifndef FILE2_H
#define FILE2_H
#include "file1.h"
#endif
|
Strategies for Debugging Errors
Using Debugging Tools
Debugging tools are essential for identifying and resolving errors. Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) often provide debugging features such as breakpoints, step-through execution, variable inspection, and call stack tracing. By leveraging these tools, you can
- Track the execution flow,
- Examine variable values,
- Identify the source of the error.
Tracing the Code:
Tracing the code involves manually examining the code's execution path to identify the point where the error occurs. This can be done by strategically inserting logs or printing statements at different parts of the code to display intermediate values or checkpoints. Observing the output or logs lets you
- track the program's flow
- identify the error's origin.
Using Print Statements
Print statements, also known as "printf" statements in languages like C/C++, are simple yet effective for debugging. By selectively adding print statements at key points in the code, you can output variable values or custom messages to the console or log files. This lets you observe the program's state during execution and locate the error.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of errors in C programming is crucial for developing reliable software. Programmers can create robust and efficient C programs by adopting good coding practices and mastering error handling. As mentioned in the above article, the right guidance and pointers can help any programmer, fresher or seasoned, easily deal with any type of error.
Wondering how you can further strengthen your programming abilities?
Check out upGrad’s Executive Post Graduate Programme in Machine Learning & AI - Now with Generative AI lectures course that can help students polish their programming skills and acquire mastery across in-demand topics such as Dall-E, ChatGPT, Graph Neural Network or GNN, and machine learning. This course provides a deeply immersive learning experience to help students advance in their careers and showcase positive future growth.
Don’t miss this opportunity, enroll now!
FAQs
1. What are the most common types of errors in C programming?
The most common error types in C include syntax, runtime, logical, semantic, linker, and preprocessor errors. Each disrupts code execution differently and must be understood clearly for efficient debugging and correction.
2. How can you identify a syntax error in C?
Syntax errors are detected during compilation. The compiler pinpoints the exact line, typically showing a descriptive error message. The error may also be caused by earlier lines with missing or incorrect syntax.
3. What is the difference between a runtime error and a logical error?
Runtime errors cause crashes during execution, often from illegal operations like division by zero. Logical errors produce incorrect results despite successful compilation, typically due to flaws in the program's logic or structure.
4. How does the linker error occur in C?
Linker errors occur when function definitions are missing, duplicate symbols exist, or incompatible object files are linked. They prevent the creation of the final executable even if the code compiles correctly.
5. Can semantic errors be compiled successfully?
Yes, semantic errors compile successfully but result in incorrect behavior during execution. These errors occur when the syntax is correct, but the logic or meaning of the statements is flawed or misleading.
6. What causes a preprocessor error in C programs?
Preprocessor errors arise from missing or incorrect directives, circular dependencies among header files, malformed macros, or faulty conditional compilation blocks like #ifdef, leading to code processing failure before compilation.
7. How can I fix a null pointer dereference error?
To fix a null pointer dereference, ensure that any pointer is properly initialized and checked for NULL before dereferencing. Always verify memory allocation success before using dynamically allocated pointers.
8. How does the order of execution lead to logical errors?
Incorrect execution order, like assigning a variable after using it, leads to logical errors. These errors are subtle and don't produce compilation errors but result in inaccurate program output.
9. What tools can help debug errors in C?
IDEs offer debugging tools like breakpoints, step-by-step execution, call stack inspection, and variable tracking. These tools help identify the source of errors effectively and speed up debugging.
10. Why do undefined symbol linker errors happen?
Undefined symbol errors happen when a function or variable is declared but not defined or linked. This usually occurs due to missing source files, libraries, or incorrect project configurations.
11. What is the role of print statements in debugging?
Print statements reveal variable values and execution flow at specific code points. They are especially useful for debugging logical and runtime errors when more advanced tools are unavailable.
12. Can aging hardware cause runtime errors?
Yes, runtime errors can result from aging or faulty hardware. Corrupted memory, failing storage, or damaged components may cause programs to behave unpredictably or crash unexpectedly during execution.
13. What is a circular dependency in header files?
A circular dependency occurs when two or more header files include each other directly or indirectly. This can cause infinite inclusion loops, leading to preprocessing and compilation errors.
14. How do Boolean expressions cause logical errors?
Incorrect Boolean expressions can mislead program control flow, causing logic errors. For example, using or instead of and in conditions can alter outcomes and produce unexpected or incorrect results.
15. What is a lexical error in C?
A lexical error occurs when the compiler encounters an invalid sequence of characters, such as an illegal symbol or malformed token, which doesn't match any valid C language grammar or identifier.
Take a Free C Programming Quiz
Answer quick questions and assess your C programming knowledge



-35c169da468a4cc481c6a8505a74826d.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)
-7f4b4f34e09d42bfa73b58f4a230cffa.webp&w=128&q=75)















%20(1)-d5498f0f972b4c99be680c2ee3b792d7.svg)











-ae8d039bbd2a41318308f8d26b52ac8f.svg)






-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)






