For working professionals
For fresh graduates
- Study abroad
More
- Executive Doctor of Business Administration from SSBM
- Doctorate in Business Administration by Edgewood College
- Doctorate of Business Administration (DBA) from ESGCI, Paris
- Doctor of Business Administration From Golden Gate University
- Doctor of Business Administration from Rushford Business School, Switzerland
- Post Graduate Certificate in Data Science & AI (Executive)
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data Analysis
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software Development
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial Excellence
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content Creation
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Human Resource Analytics Course from IIM-K
- Directorship & Board Advisory Certification
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- CSM® Certification Training
- CSPO® Certification Training
- PMP® Certification Training
- SAFe® 6.0 Product Owner Product Manager (POPM) Certification
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps
- Python Programming Course
- Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full Stack
- AWS Solutions Architect Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
- AWS Technical Essentials
- The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from Microsoft
5. Array in C
13. Boolean in C
18. Operators in C
33. Comments in C
38. Constants in C
41. Data Types in C
49. Double In C
58. For Loop in C
60. Functions in C
70. Identifiers in C
81. Linked list in C
83. Macros in C
86. Nested Loop in C
97. Pseudo-Code In C
100. Recursion in C
103. Square Root in C
104. Stack in C
106. Static function in C
107. Stdio.h in C
108. Storage Classes in C
109. strcat() in C
110. Strcmp in C
111. Strcpy in C
114. String Length in C
115. String Pointer in C
116. strlen() in C
117. Structures in C
119. Switch Case in C
120. C Ternary Operator
121. Tokens in C
125. Type Casting in C
126. Types of Error in C
127. Unary Operator in C
128. Use of C Language
C Program to Find ASCII Value of a Character
“How to find the ASCII value of a character in C?” or “How to print ASCII value in C?” Are these some of the many questions bothering you? Well then, worry no more.
Here is a detailed guide to everything you need to know about ASCII values. In this guide, we will learn to write a C program to find the ASCII value of a character using different methods. And that’s not all — we will also explore its multiple usages in the C programming language.
So, without any further ado, let’s get started!
Want to make your career is software engineering. Explore the upGrad's top Software Engineering Courses that are taught by the industry experts and top-faculty.
What is ASCII code?
Since its inception in 1960, American Standard Code For Information Interchange or ASCII has received global recognition as a character encoding standard used in communication systems and computers.
A unique numeric code is assigned for each character, which can be anywhere between the range of 0-127. This includes various characters such as uppercase and lowercase, control characters, punctuation marks, and special symbols as well.
For example, while the ASCII code for the uppercase letter A is 65, the ASCII code for the lowercase letter ‘a’ is 97.
They are usually represented in the binary format, wherein each code is a 7-bit binary number. However, in today’s modern computing systems, they are represented using 8 bits (1 byte), the most significant bit being zero.
Let’s navigate other components to analyze this encoding standard in depth.
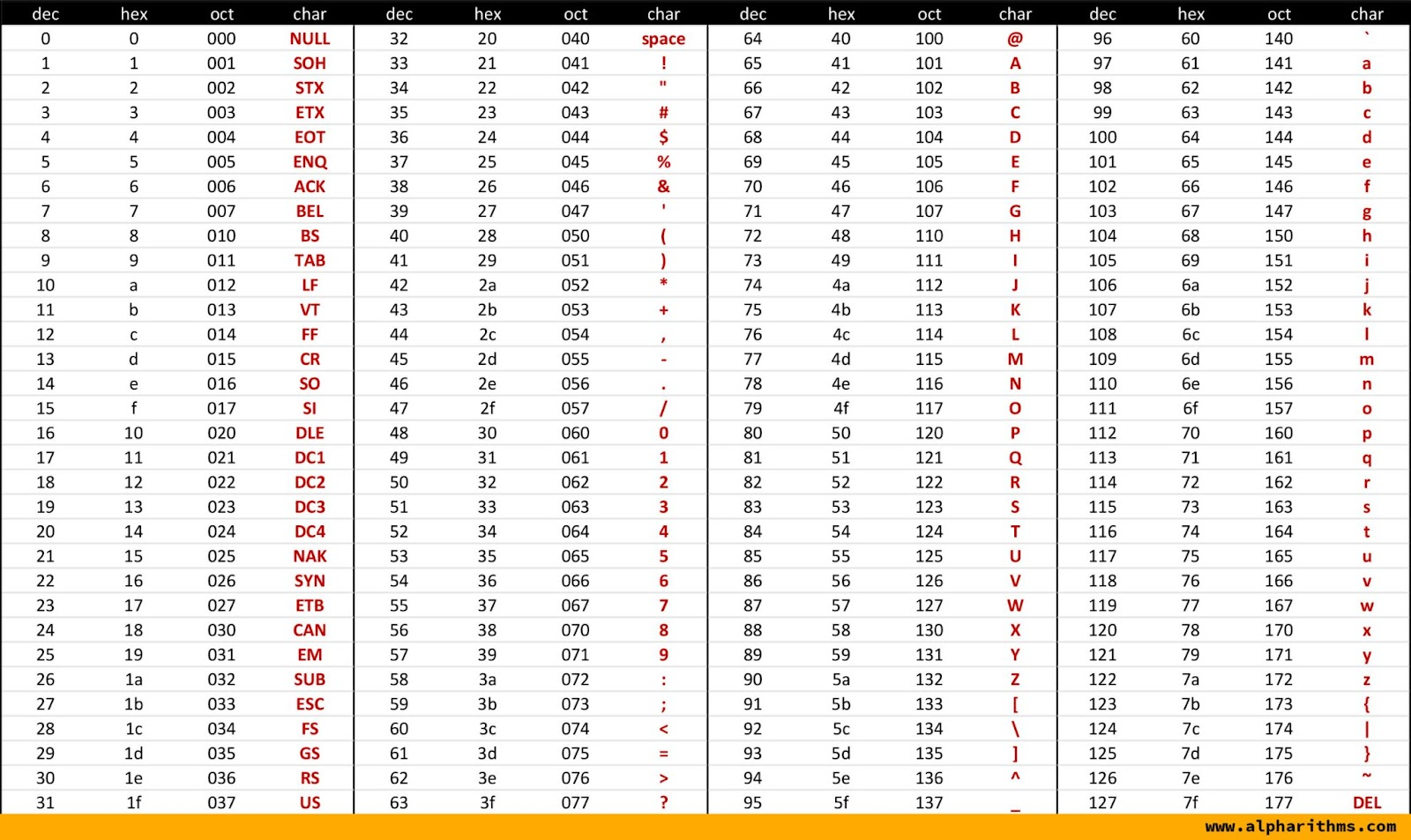
ASCII Table
Simply put, an ASCII table can be defined as a reference chart that contains ASCII codes and their corresponding characters. It can be extremely beneficial when you are trying to look up specific characters and their codes.
An ASCII table consists of multiple columns, each highlighting some aspects of the characters. Let's look at some of the most common columns you will likely encounter in an ASCII table.
- Decimal - As the name suggests, the decimal column contains the numeric value that is assigned to each character.
- Hexadecimal - It highlights the ASCII codes in base 16 formats.
- Octal - The ASCII codes in this column are highlighted in base-8 format.
- Character - It typically consists of various characters in correspondence to the ASCII codes. They may range from special characters to symbols and letters.
- Description - It usually contains a brief description or name of each character. Sometimes, it also specifies the function or purpose of a character.
The ASCII table is easily accessible through any programming documentation, textbook, or even online. It can prove to be extremely useful, especially when you are trying to work with ASCII characters, encoding, or simply trying to understand the relationship between numeric codes and characters.
Conversion of Character to ASCII Value
Converting a character into its corresponding ASCII value is a common programming phenomenon. In most programming languages, you can achieve this by simply using the built-in functions or methods provided by the language.
Using Type Casting to Convert Character to ASCII Value
A few programming languages use type casting to convert characters into ASCII values. Such include C++ and Java, among others.
However, please note that type casting is only possible in C++ because the characters are internally represented as integers in ASCII or Unicode. Not all programming languages can support direct type casting from characters to integers. In such cases, you might need to use language-specific functions to obtain the ASCII value of a character.
C Program to Find ASCII Value of a Character (3 Methods)
To understand this example, you should have knowledge of the following C programming topics:
- Data Types In C
- Constants, Literals, and Variables in C
- Input Output (I/O) in C
There are multiple ways to find the ASCII value of a character in C. Let’s go through the 3 most commonly used methods with examples and output.
Method 1: Using %d Format Specifier with printf()
This is the simplest way where we directly print the ASCII value of a character using %d.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'A'; // character to check
printf("The ASCII value of %c is %d\n", ch, ch);
return 0;
}
Output:
The ASCII value of A is 65
Explanation:
- %c prints the character, and %d prints its integer value.
- Since characters are internally stored as integers in C, ch directly gives its ASCII value when printed with %d.
Method 2: Taking Character Input from User
In this approach, we allow the user to enter any character at runtime and then print its ASCII value.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch;
printf("Enter a character: ");
scanf("%c", &ch); // take character input
printf("The ASCII value of %c is %d\n", ch, ch);
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Enter a character: g
The ASCII value of g is 103
Explanation:
- We use scanf("%c", &ch) to read a single character from the user.
- printf() then displays both the character and its ASCII equivalent.
Method 3: Using Typecasting
You can also explicitly cast a character to int to get its ASCII value, though C does this implicitly too.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
char ch = 'z';
int ascii = (int) ch; // typecasting char to int
printf("The ASCII value of %c is %d\n", ch, ascii);
return 0;
}
Output:
The ASCII value of z is 122.
Explanation:
- (int) ch forces the compiler to treat ch as an integer.
- The resulting integer value is stored in ascii, which is then printed.
Application of ASCII Values in C Programming
Now that you are familiar with the process of using a C program to find ASCII value of a character let’s take a look at some of the applications of ASCII values in C programming.
Character Operations using ASCII Values
You can perform various character operations in C programming using ASCII values. Such include,
- Converting Case: Converting a character from uppercase to lowercase is very easy. You simply have to manipulate the ASCII value. For example, if you wish to convert it into an uppercase, you can subtract 32 from its ASCII value. Simultaneously, if you want to convert it into a lowercase character, you can add 32. Let’s take a look at this example,
char c = 'a'; |
- Comparing Character: To compare characters, you must first compare their ASCII values. For example, to check whether a character is an uppercase letter or not, you can take the help of a comparison operator, such as (‘<’ and ‘>’) with the appropriate ASCII value ranges.
- Arithmetic Operations: By simply adding or subtracting a number from a character, you can shift it to a completely different character. Here is a small example of the same.
char c = 'A'; |
The output generated is D.
String Operations using ASCII Values
Simply put, a string is an array of characters. You can use ASCII values to perform a wide range of string operations in C programming. The following list contains some of the most commonly performed ones.
- String Comparison - By analysing the ASCII value of two characters, you can compare two strings. To achieve the same, you can make use of library functions such as ‘strcmp()’. The algorithm for the same goes as follows,
#include <stdio.h> |
However, please note that apart from this, you can also compare strings by manually comparing two individual characters.
- String Length - You can also accurately determine the length of a string using ASCII values. The idea is to count the characters until you reach the null character ('\0').
- String Manipulation - Last but not least, string manipulation is also achievable through ASCII values. It enables the execution of a variety of tasks ranging from altering the case of characters to replacing characters, among other transformations.
File Operations using ASCII Values
From reading to writing, you can perform multiple file operations using ASCII values in C programming. A few such include,
Reading and Writing Characters To A File - To read or write a character to a file, we typically use the getc() and putc() I/O functions. The syntax for the same goes as follows,
getc()
char ch = getc(fptr);
putc()
putc(ch, fptr)
You need to first create a file pointer and select any filename of your choice. Following this, you can then use the putc() function to write characters to the file. After this has been done successfully, you can then move on to the getc() function to read the file data and display the same on the console.
Conclusion
To sum up, ASCII values play a significant role in C programming. From character representation to string manipulation, and standardisation, the usage of ASCII values in C ranges diversely. It enables programmers to perform various tasks and comparisons based on their values. Furthermore, a complete understanding of ASCII values and their usage in C programming also helps you to work with strings and file operations more effectively.
While grasping the basics of ASCII, check out upGrad’s Full Stack Software Development Bootcamp, which will further help you advance your technical skills and pave the way to explore a thriving career in development!
FAQs
1. How to get ASCII value of a character in C?
To get the ASCII value of a character in C, you can use a simple printf statement with %d format specifier. For example, printf("%d", ch); will print the ASCII value of the character stored in variable ch.
2. How to convert a character to ASCII in C?
To convert a character to ASCII in C, store the character in a variable and print it using %d. This treats the character as an integer and displays its corresponding ASCII value in the output.
3. How to get ASCII value in C using user input?
Use scanf to take a character as input from the user and then print it using %d to get the ASCII value in C. This method helps you dynamically check the ASCII code of any typed character.
4. How to store ASCII value of char in C?
You can store the ASCII value of a char in an int variable by assigning the character directly to the int. For example:
int ascii = 'A';
This stores the ASCII value of 'A' (65) in the ascii variable.
5. What is the ASCII value of 'a' to 'z' in C?
In C, the ASCII value of lowercase 'a' to 'z' ranges from 97 to 122. These values are sequential, so you can loop through characters to display or work with each alphabet and its corresponding code.
6. How to convert char to ASCII in C with code example?
Assign the character to an int variable or print it using %d. Example:
char ch = 'K';
printf("ASCII: %d", ch);
This prints the ASCII value of 'K', which is 75.
7. How to get ASCII value of char in C without using functions?
You don't need any special function to get ASCII value in C. Just use the %d specifier in printf to output the integer equivalent of a character directly from a char variable.
8. Can I convert multiple characters to ASCII in C?
Yes, you can use a loop to convert multiple characters to ASCII values in C. Iterate through a character array and print each character’s ASCII using %d inside the loop.
9. Is it possible to perform operations on ASCII values in C?
Yes, since characters are stored as integers in C, you can perform arithmetic operations on them. For example, 'A' + 1 gives 'B', as ASCII values increase sequentially for alphabets.
10. How to get the ASCII value of user-defined character in C?
Use scanf("%c", &ch); to take a character input from the user, then print ch using printf("%d", ch); to get the ASCII value of a character in C.
11. Why is it useful to convert characters to ASCII in C?
Converting characters to ASCII in C is helpful for encryption, sorting, or performing logical checks. It allows you to treat characters as numeric data and apply custom algorithms or conditions based on their codes.
-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)
Take a Free C Programming Quiz
Answer quick questions and assess your C programming knowledge


Author|900 articles published


upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 9 AM to 12 AM (midnight)
Indian Nationals
1800 210 2020
Foreign Nationals
+918068792934
Disclaimer
1.The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
2.The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not provide any a.