For working professionals
For fresh graduates
- Study abroad
More
- Executive Doctor of Business Administration from SSBM
- Doctorate in Business Administration by Edgewood College
- Doctorate of Business Administration (DBA) from ESGCI, Paris
- Doctor of Business Administration From Golden Gate University
- Doctor of Business Administration from Rushford Business School, Switzerland
- Post Graduate Certificate in Data Science & AI (Executive)
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Data Analysis
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Software Development
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Managerial Excellence
- Gen AI Mastery Certificate for Content Creation
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Human Resource Analytics Course from IIM-K
- Directorship & Board Advisory Certification
- Gen AI Foundations Certificate Program from Microsoft
- CSM® Certification Training
- CSPO® Certification Training
- PMP® Certification Training
- SAFe® 6.0 Product Owner Product Manager (POPM) Certification
- Post Graduate Certificate in Product Management from Duke CE
- Professional Certificate Program in Cloud Computing and DevOps
- Python Programming Course
- Executive Post Graduate Programme in Software Dev. - Full Stack
- AWS Solutions Architect Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials
- AWS Technical Essentials
- The U & AI GenAI Certificate Program from Microsoft
6. JDK in Java
7. C++ Vs Java
16. Java If-else
18. Loops in Java
20. For Loop in Java
46. Packages in Java
53. Java Collection
56. Generics In Java
57. Java Interfaces
60. Streams in Java
63. Thread in Java
67. Deadlock in Java
74. Applet in Java
75. Java Swing
76. Java Frameworks
78. JUnit Testing
81. Jar file in Java
82. Java Clean Code
86. Java 8 features
87. String in Java
93. HashMap in Java
98. Enum in Java
101. Hashcode in Java
105. Linked List in Java
109. Array Length in Java
111. Split in java
112. Map In Java
115. HashSet in Java
118. DateFormat in Java
121. Java List Size
122. Java APIs
128. Identifiers in Java
130. Set in Java
132. Try Catch in Java
133. Bubble Sort in Java
135. Queue in Java
142. Jagged Array in Java
144. Java String Format
145. Replace in Java
146. charAt() in Java
147. CompareTo in Java
151. parseInt in Java
153. Abstraction in Java
154. String Input in Java
156. instanceof in Java
157. Math Floor in Java
158. Selection Sort Java
159. int to char in Java
164. Deque in Java
172. Trim in Java
173. RxJava
174. Recursion in Java
175. HashSet Java
177. Square Root in Java
190. Javafx
Number Pattern Program in Java
Introduction
Java's flexibility and robustness set it apart. Yet its true prowess comes to light when creating number pattern programs in Java. These programs, integral to Java learning, underpin the essence of nested loops and control statements. They also offer a stepping stone to understanding algorithms - the heart of computational thinking. They sharpen your ability to structure logic while coding and hone your debugging skills. To take Java expertise to a whole new level, learning number pattern programs in Java becomes an absolute necessity. This discourse aims to enlighten you about the importance and intricacies of these programs, leading you onto the path of true Java mastery.
Overview
In the realm of coding, number pattern programs in Java hold a special place. They're miniature puzzles demanding logical thinking and a clear understanding of Java syntax. The road to understanding them may seem steep, yet the view from the top is worth the climb. This guide offers a map to this road, laying out a clear path to conquering number pattern programs in Java. It will present examples of commonly used patterns, explain their logic and structure, and show how to code them efficiently. This guide will also introduce advanced patterns, pushing the boundaries of your Java skills.
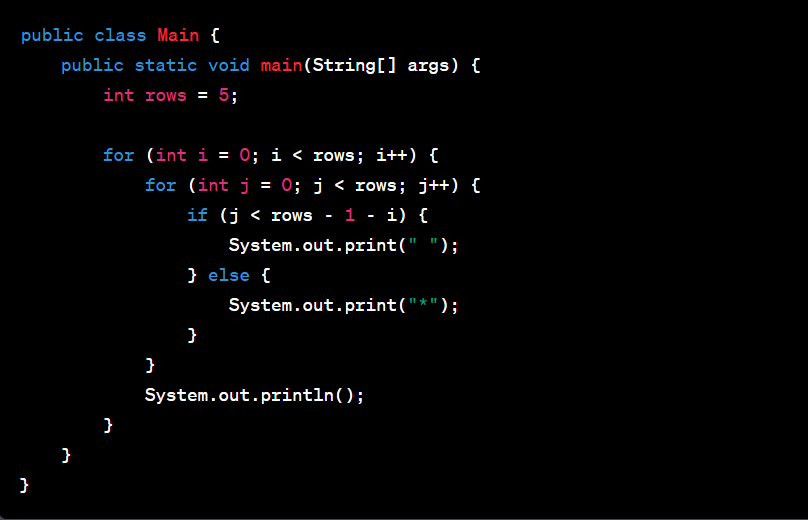
Top Java Number Pattern Program
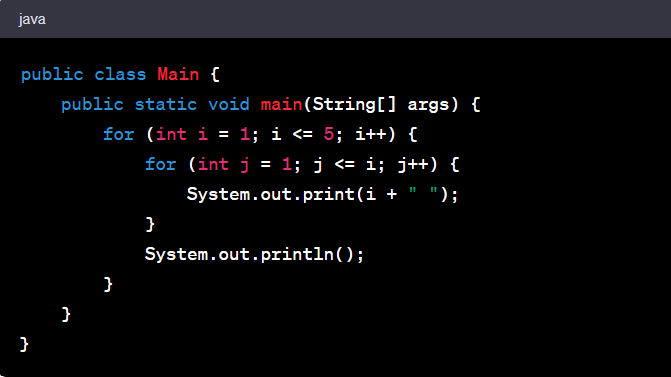
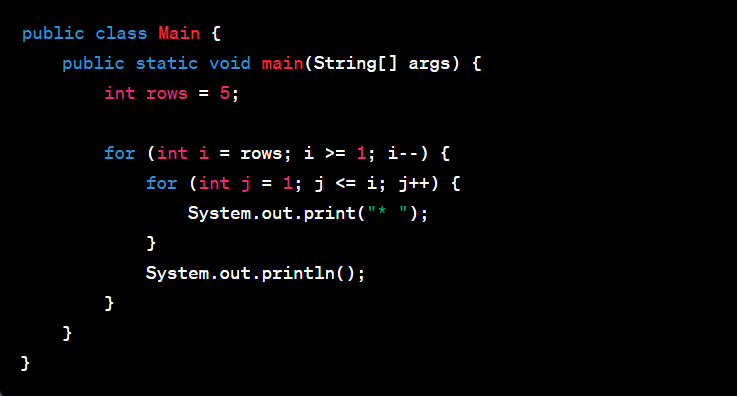
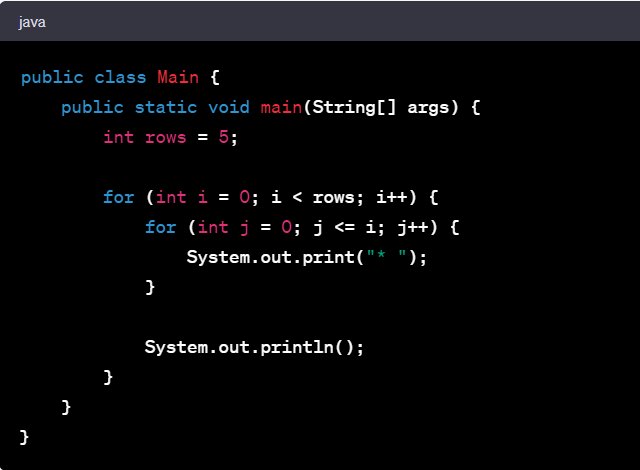
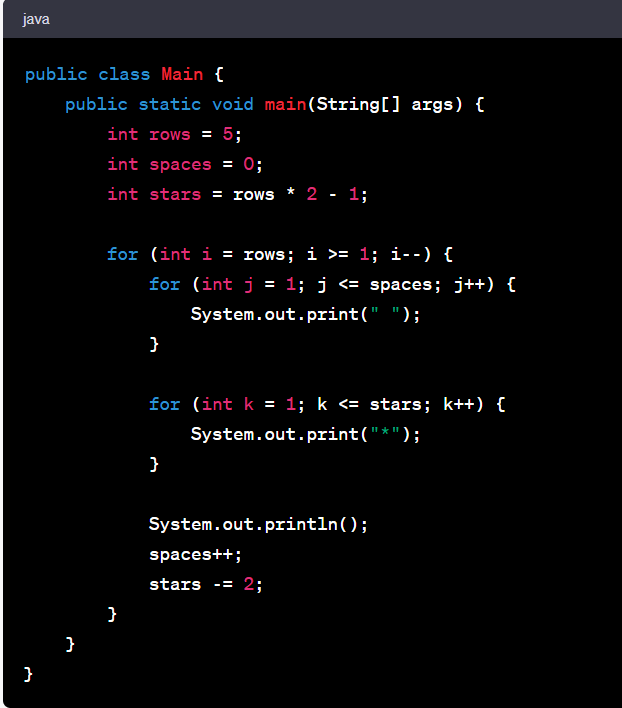
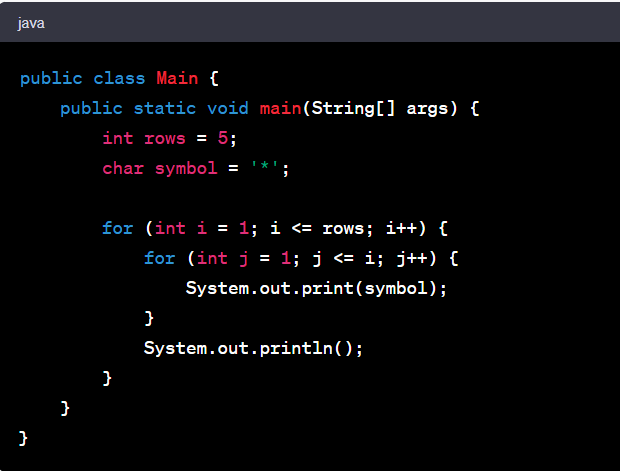
One of the top Java number pattern programs is the Pyramid pattern. This pattern is a classic exercise for beginners. It uses nested loops to create an impressive pyramid-like shape made of numbers. Understanding this program bolsters your logic and mastery of nested loops.
Let's explore a simple Pyramid pattern in Java:
The code for this Pyramid pattern in Java is:
This code utilizes two for-loops. The outer loop controls the number of rows, while the inner loop controls how many times the number prints in each row. It's a beautiful blend of logic and code execution. This pattern program offers an engaging way to understand the power of nested loops in Java and forms a fundamental stepping stone in your journey of mastering Java programming.
Java Pattern Program
In Java, pattern programs involve nested loops, where each loop serves a specific purpose. They're an excellent way to understand how loops work, especially when one loop is nested inside another. A solid understanding of these concepts can greatly enhance your proficiency in Java.
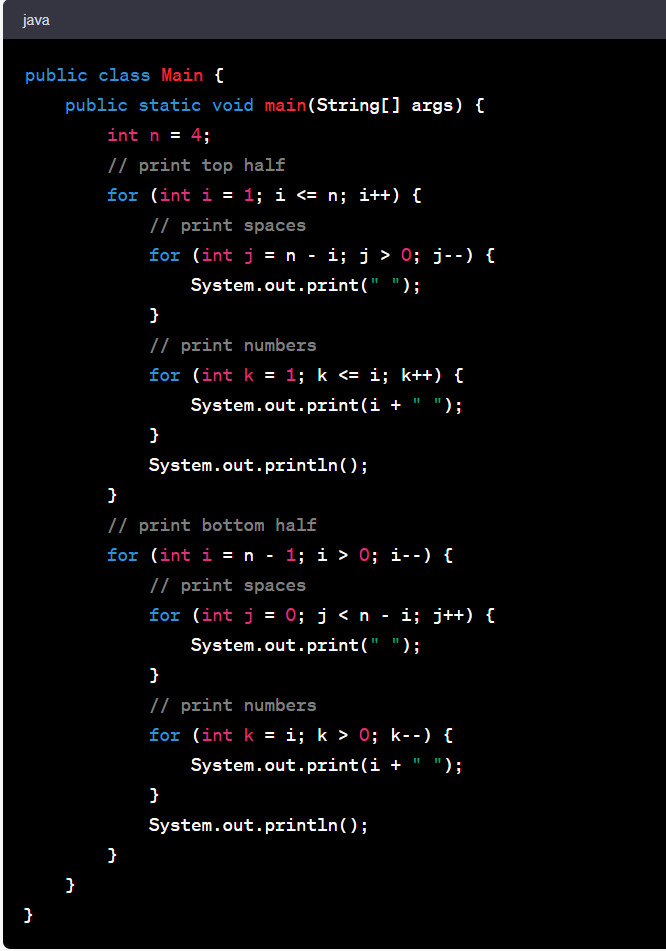
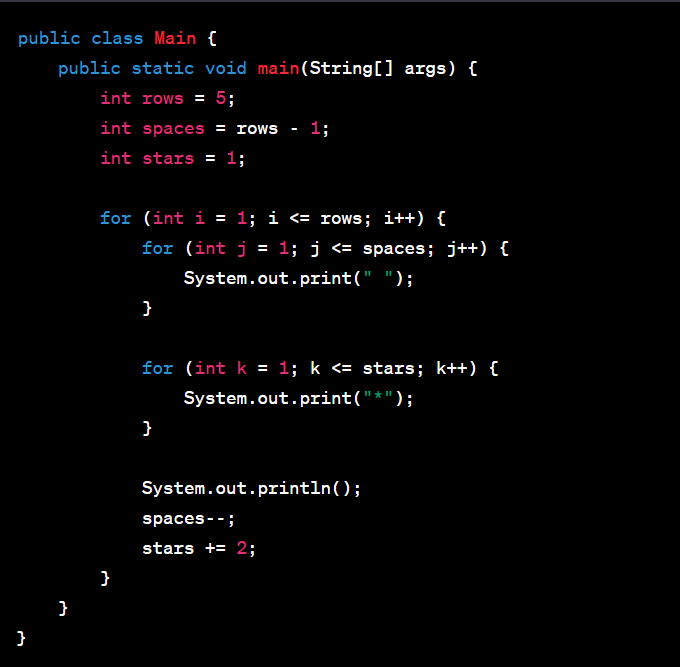
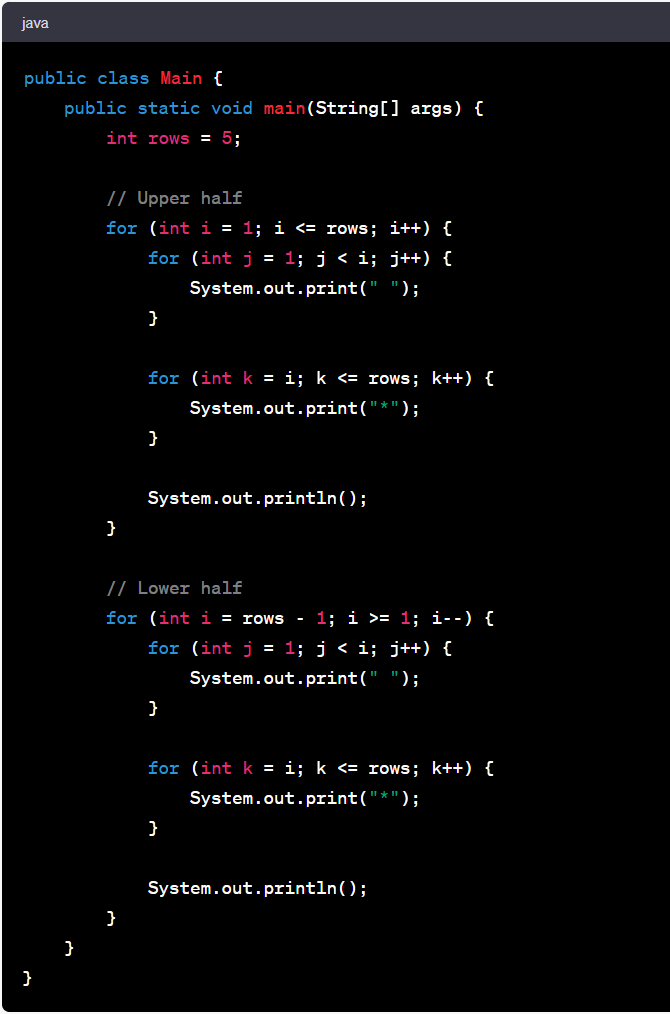
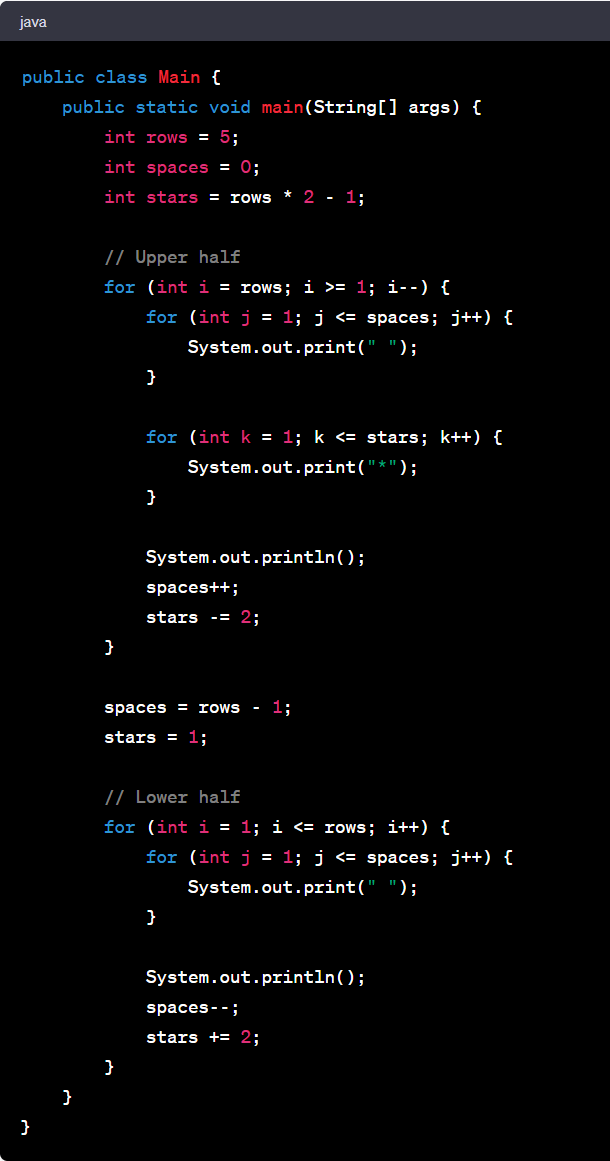
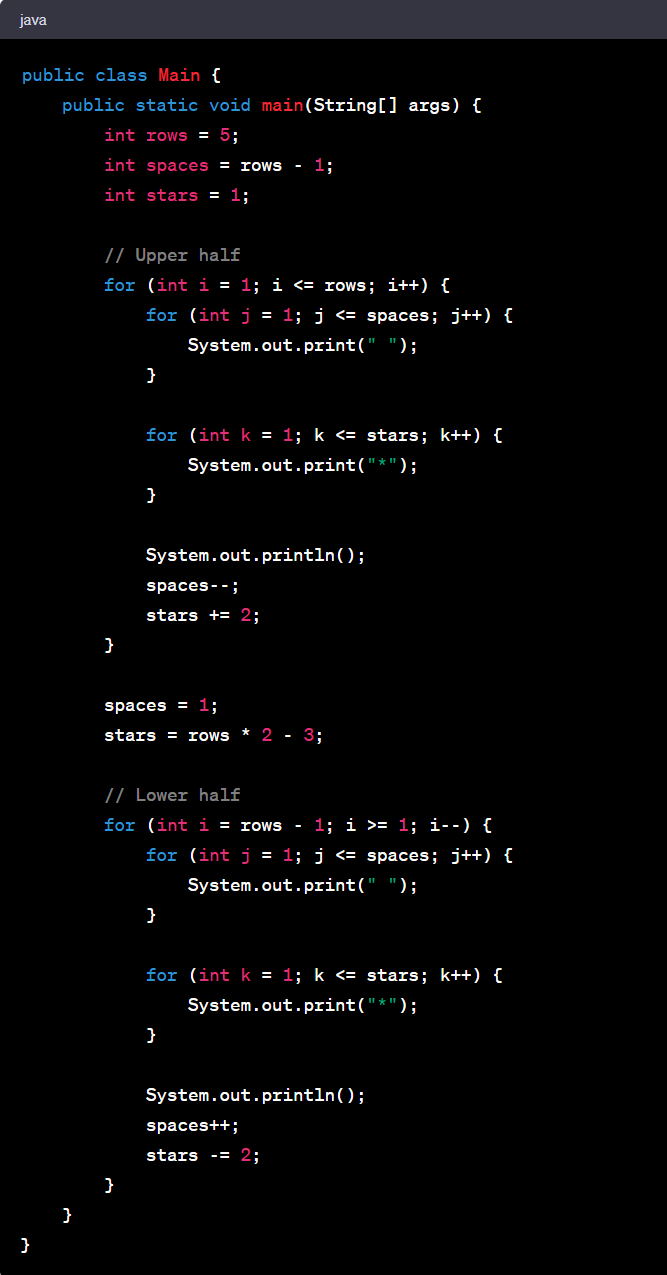
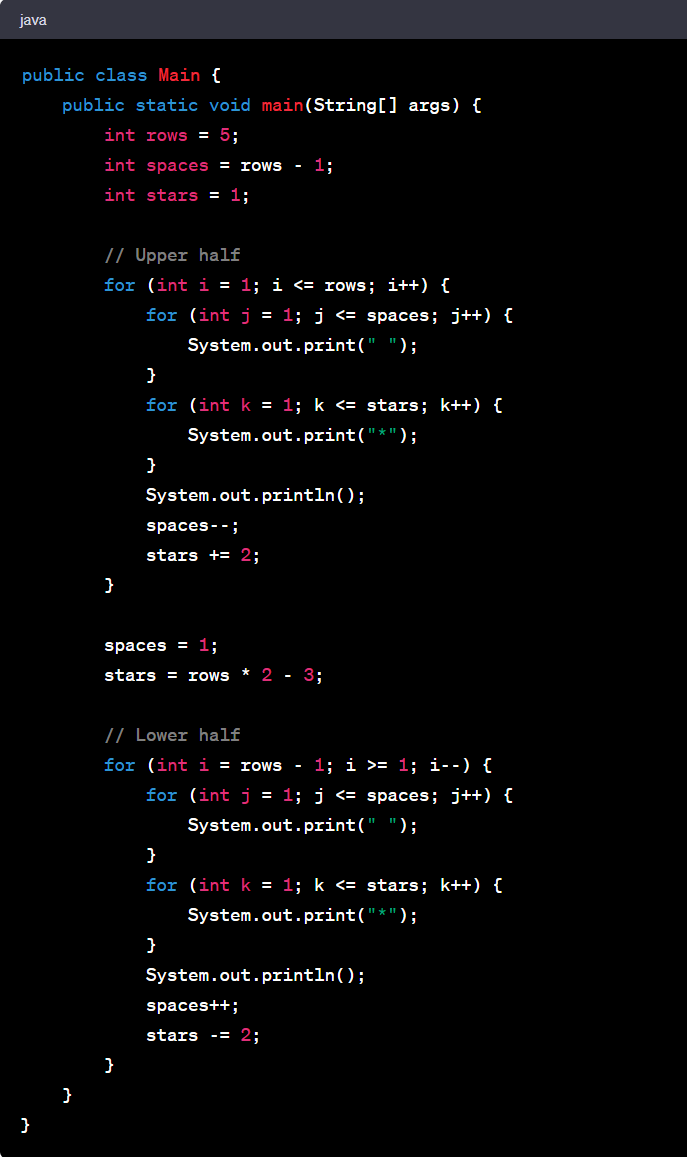
Let's delve into the Diamond pattern. It's a bit more complex than the previous example, but highly enriching to understand.
Consider a Diamond pattern:
This pattern can be coded in Java as follows:
This pattern program uses nested loops to create the diamond shape. The first outer loop and its nested loops create the top half of the diamond, while the second outer loop and its nested loops create the bottom half. The logic for spaces and the number to print is determined by the loop variables.
Some Other Number Pattern Programs In Java
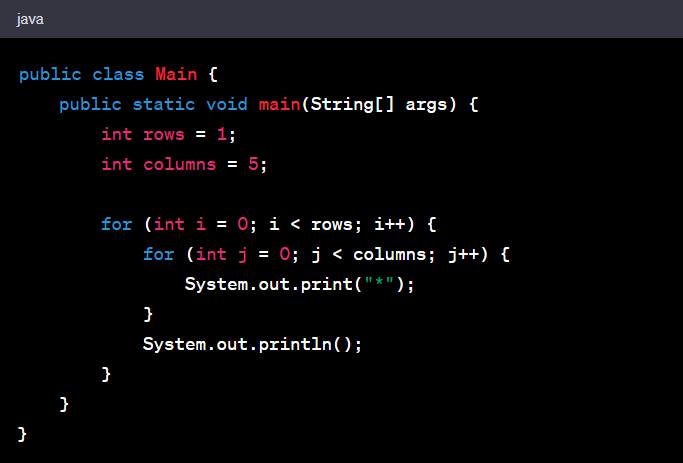
1. Start Pattern
This pattern is formed by printing a sequence of asterisks in a horizontal line.
Example
Code:
2. Right Triangle Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern forms a right triangle with asterisks, where each row has one more asterisk than the previous row.
Example:
Code:
3. Left Triangle Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern creates a left-aligned triangle with asterisks, where each row has the same number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
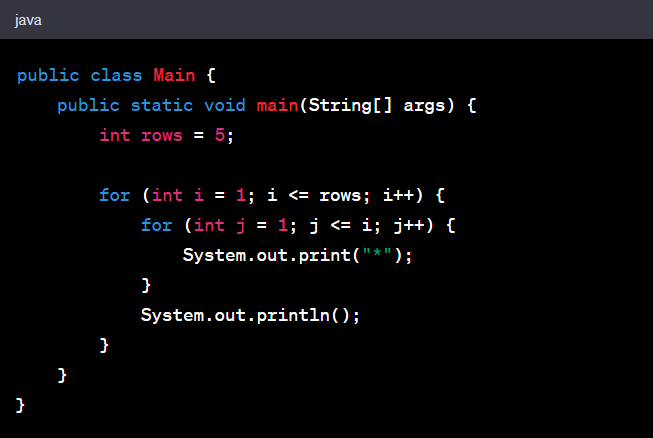
4. Pyramid Star Pattern
This pattern creates a pyramid-like structure with asterisks, where each row has a gradually increasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
5. Diamond Shape Pattern
This pattern forms a diamond shape with asterisks, consisting of both ascending and descending rows of asterisks.
Example:
Code
6. Mirrored Right Triangle Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern creates a right-aligned triangle with asterisks, where each row has a decreasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
7. Reverse Pyramid Pattern in Java
This pattern forms an inverted pyramid with asterisks, where each row has a gradually decreasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
8. Downward Triangle Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern forms a downward-facing triangle with asterisks, where each row has a gradually decreasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
9. Right Down Mirror Star Pattern
This pattern forms a right-aligned triangle with asterisks, where each row has a decreasing number of asterisks, and the pattern is mirrored vertically downward.
Example:
Code
10. Right Pascal's Triangle
This pattern represents Pascal's Triangle using asterisks, where each row corresponds to the coefficients of the binomial expansion.
Example:
Code
11. Left Pascal's Triangle
This pattern represents Pascal's Triangle using asterisks, where each row corresponds to the coefficients of the binomial expansion.
Example:
Code
12. Sandglass Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern forms a sandglass shape with asterisks, consisting of both ascending and descending rows of asterisks.
Example:
Code
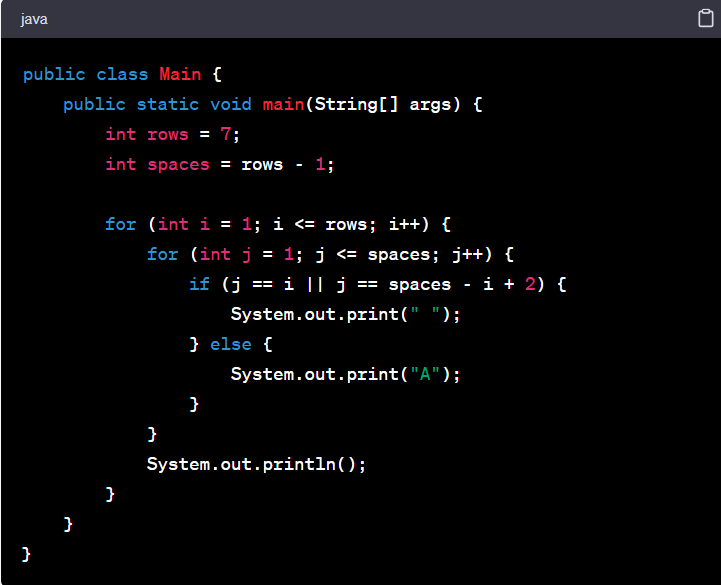
13. Alphabet Pattern Program in Java
This pattern forms the shape of an alphabet letter using asterisks.
Example for the letter 'A':
Code
14. Triangle Star Pattern Program in Java
This pattern forms a triangle shape with asterisks, where each row has a gradually increasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
15. Down Triangle Pattern
This pattern forms a downward-facing triangle shape with asterisks, where each row has a gradually decreasing number of asterisks.
Example:
Code
16. Diamond Star Pattern
This pattern forms a diamond shape with asterisks, consisting of both ascending and descending rows of asterisks.
Example
Code
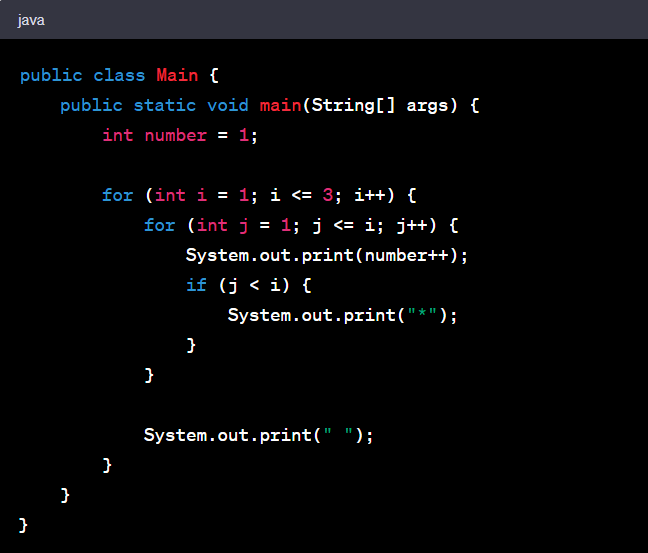
1 2*3 4*5*6 Pattern Printing In Java
To print the "1 23 45*6" pattern in Java, you can use the following code:
Output
In this code, we use nested loops to control the pattern. The outer loop runs for three iterations, representing the three groups of numbers. The inner loop prints the numbers and asterisks in each group. The ‘number’ variable is incremented after each number is printed. We check whether to print an asterisk based on the condition ‘j < i’ to ensure that an asterisk is not printed after the last number in each group.
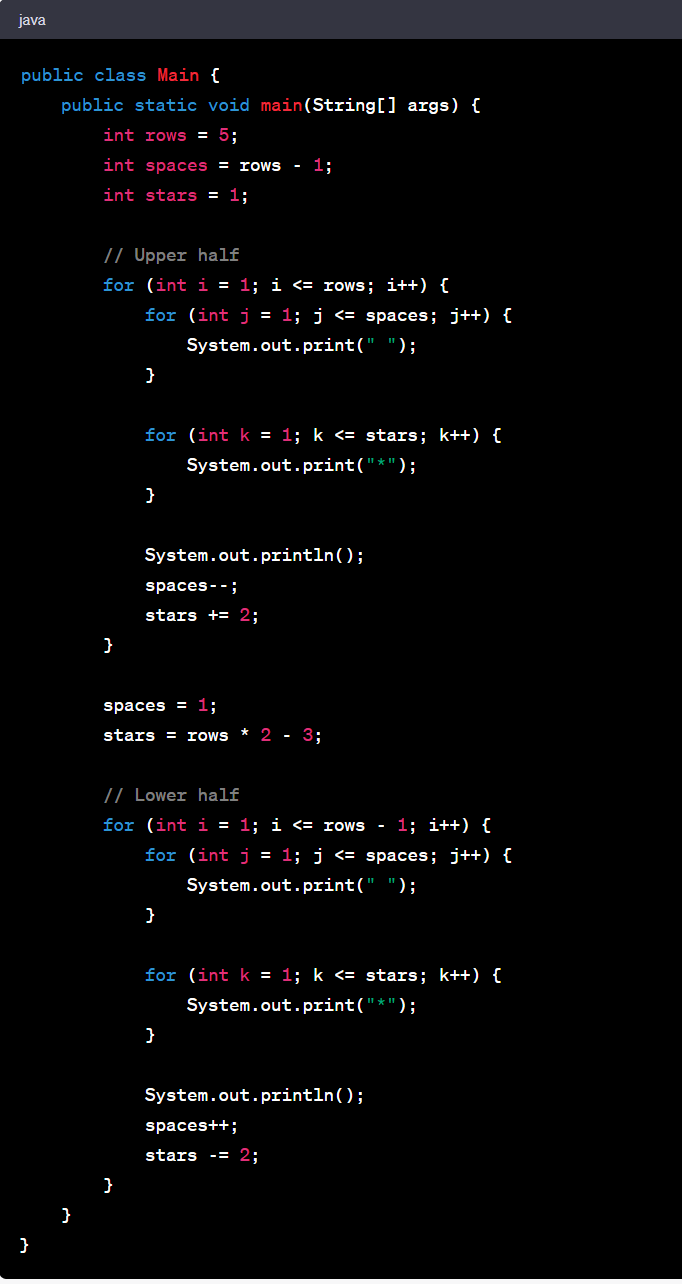
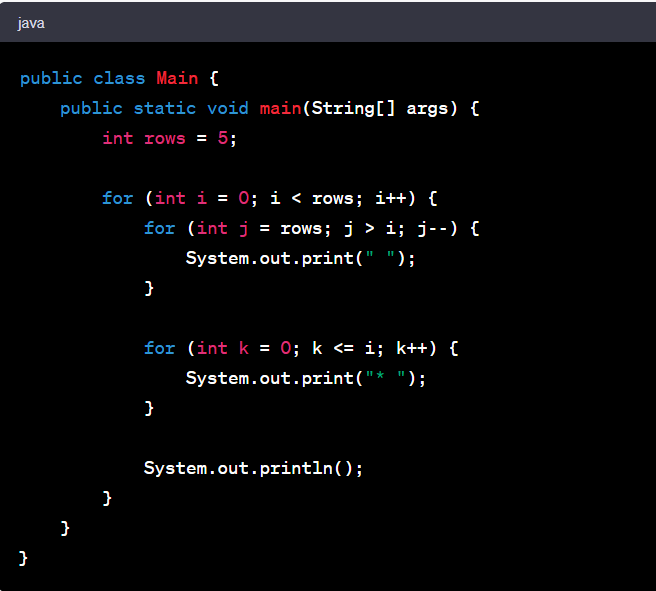
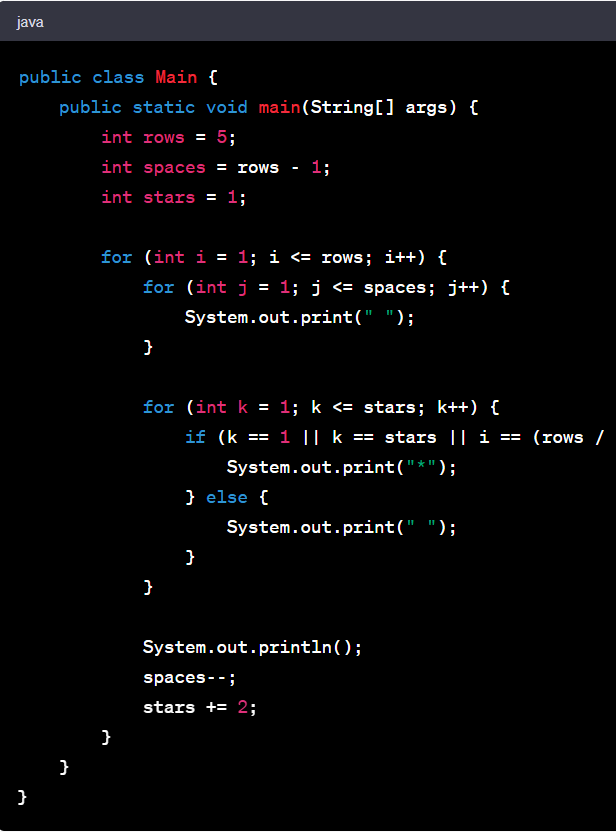
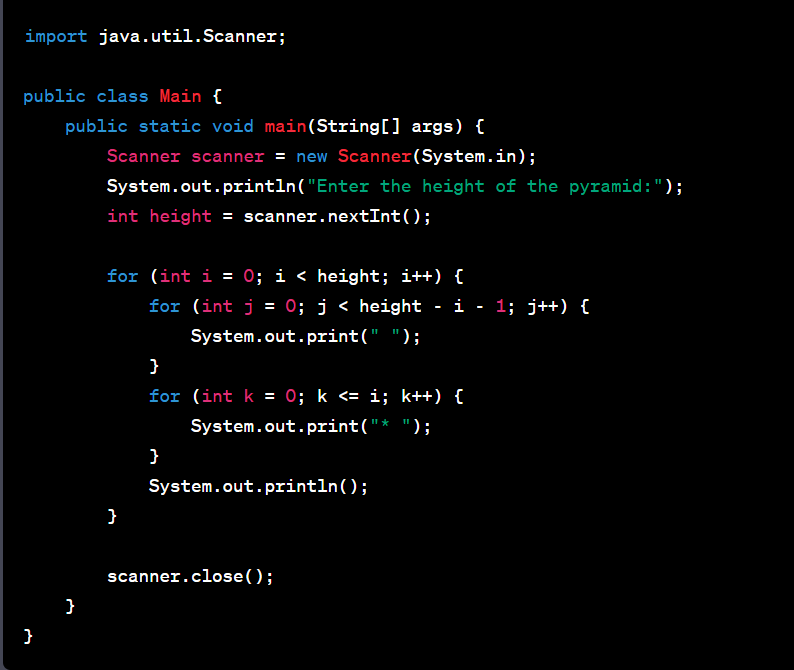
Pyramid Program In Java Using Scanner
Here's a simple Java program that uses the Scanner class to take an integer input from the user and print a pyramid of that height:
In this program, the outer loop for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) controls the number of lines in the pyramid, which is equal to the height input by the user.
The inner loops print each line of the pyramid. The first inner loop for (int j = 0; j < height - i - 1; j++) prints the leading spaces, and the second inner loop for (int k = 0; k <= i; k++) prints the stars. The number of stars in each line is one more than the line number (assuming the first line number is 0).
Please note that the height of the pyramid is entered by the user through the console. So, when you run this program, it will wait for your input. After entering a number, the program will print a pyramid of that height.
The output will depend on the number entered by the user. Let's say the user enters 5, the output will be:
This is a pyramid of height 5. Each line contains stars separated by a space, and the number of stars in each line is equal to the line number (starting from 1). The leading spaces on each line create the pyramid shape. The number of leading spaces is equal to the difference between the height of the pyramid and the line number.
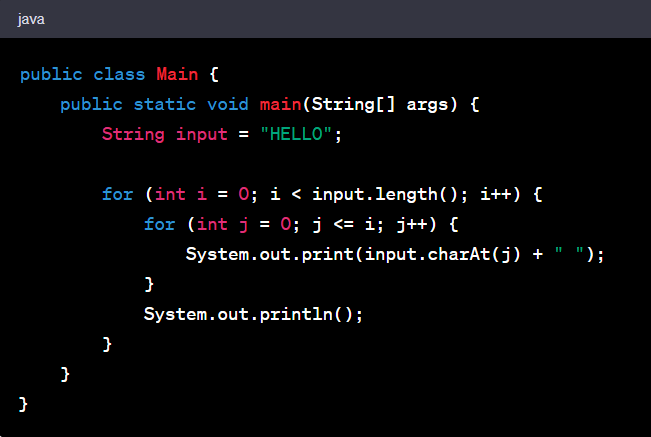
String Pattern Program In Java
Here's an example of a string pattern program in Java that prints a specific pattern:
Output
In this program, we have a string ‘input’ containing the word "HELLO". We use two nested loops to iterate over the characters of the string and print the pattern. The outer loop controls the number of rows, and the inner loop prints the characters up to the current row. We use the ‘charAt()’ method to access each character in the string. Finally, we print a space after each character to separate them.
You can modify the ‘input’ variable to any string of your choice, and the program will generate the corresponding pattern.
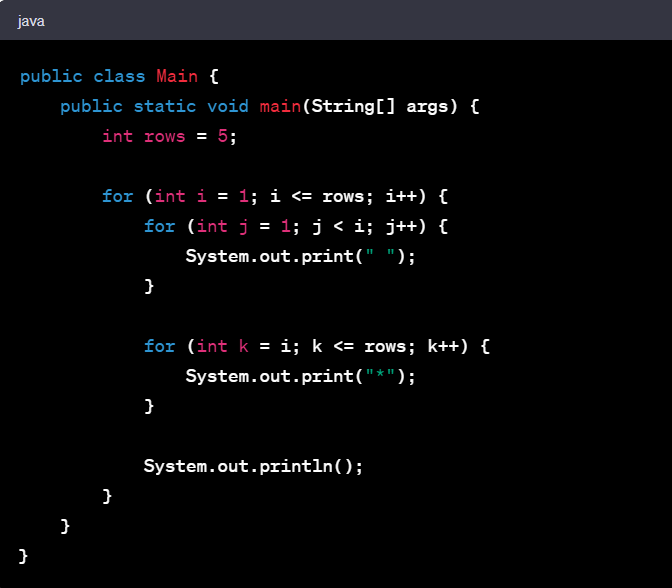
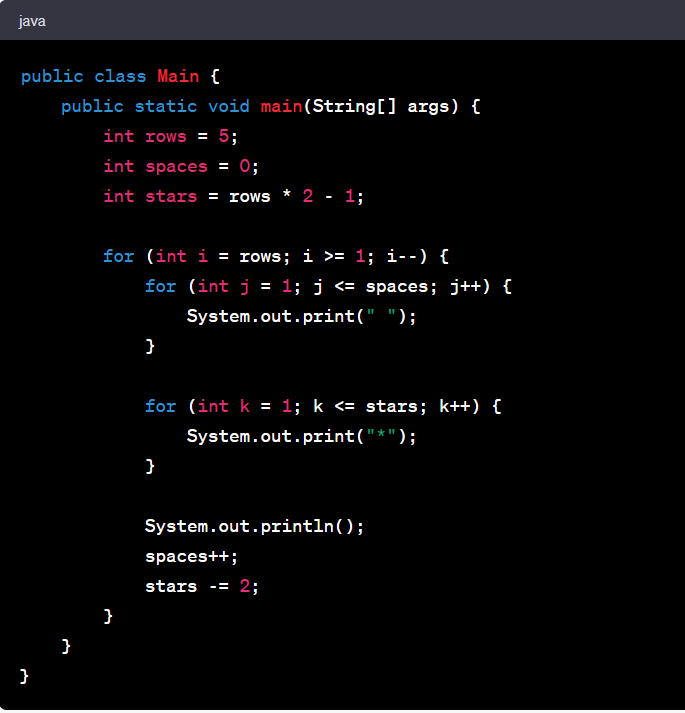
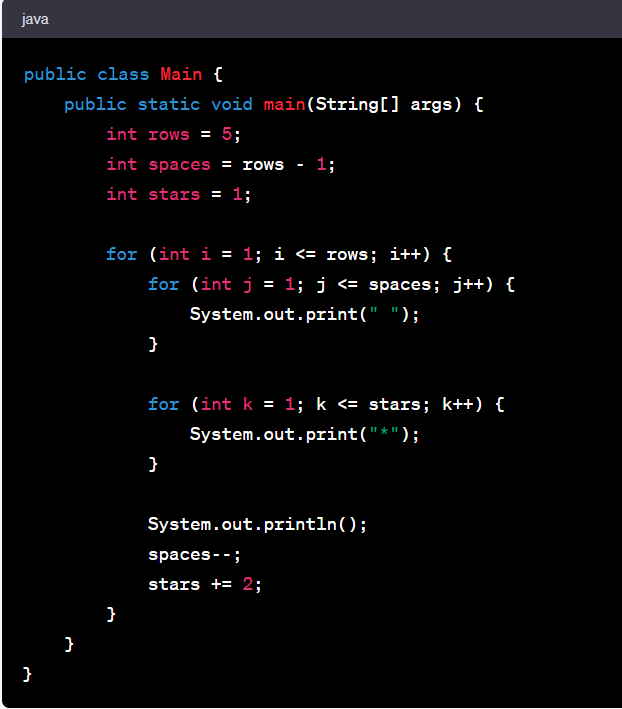
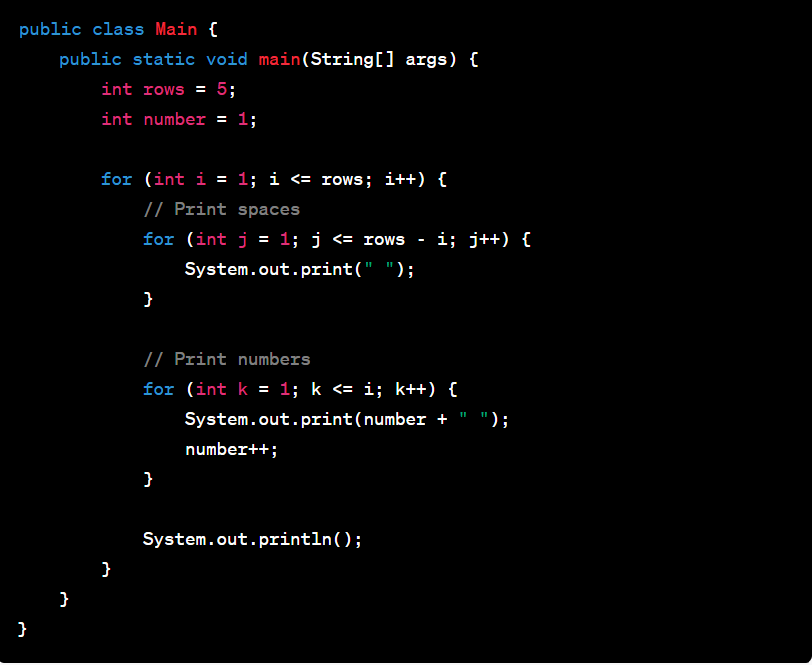
Number Triangle Pattern In Java
A number triangle pattern in Java refers to a pattern where a series of numbers are arranged in the shape of a triangle. Each row of the triangle contains numbers that follow a specific pattern or sequence. The pattern starts with a single number in the first row and gradually adds more numbers in subsequent rows.
Here's an example of a number triangle pattern program in Java:
Output:
In this program, we have a variable ‘rows’ which represents the number of rows in the triangle. We also have a variable ‘number’ to keep track of the current number to be printed.
We use two nested loops to control the printing of spaces and numbers. The outer loop iterates over the rows, and the inner loops handle the spaces and numbers within each row.
The first inner loop prints the spaces before the numbers, based on the row number. The second inner loop prints the numbers, incrementing the ‘number’ with each iteration.
Character Pattern in Java
A "Character Pattern Program in Java" refers to a pattern formed by arranging characters or symbols in a specific shape or sequence. Instead of numbers, this type of pattern involves using characters, such as alphabets, symbols, or any other printable characters available in Java.
Character patterns in Java can be created using nested loops and string manipulation techniques. The pattern can take various forms, including triangles, rectangles, diamond shapes, or even custom shapes based on specific characters or symbols.
Here are a few examples of character pattern programs in Java
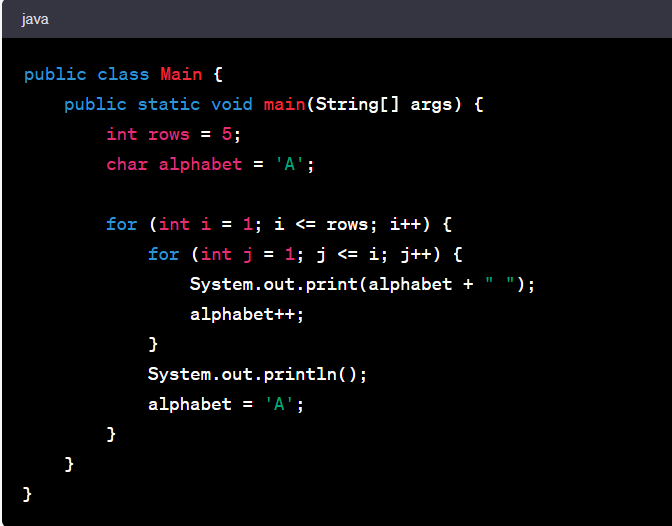
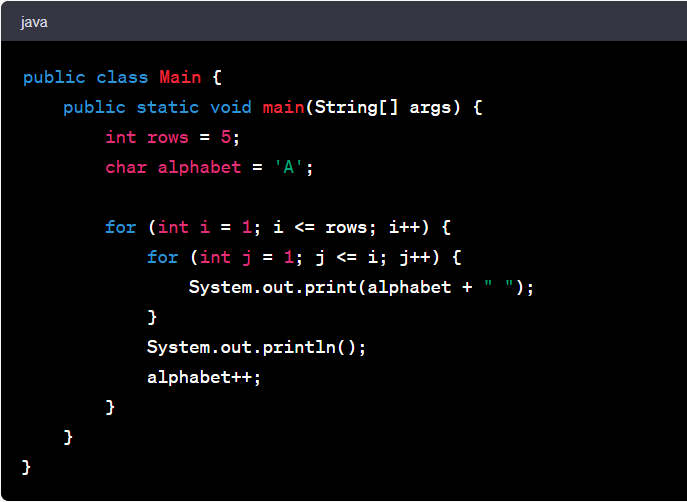
1. Right Triangle Alphabetic Pattern
This pattern forms a right triangle using alphabets, where each row has one more alphabet than the previous row.
Example:
Code
2. Repeating Alphabet Pattern
This pattern creates a pattern where a given alphabet is repeated in each row.
Example:
Code
3. K-shape Alphabet Pattern
This pattern forms the shape of the letter 'K' using the alphabet.
Example:
Code
4. Triangle Character Pattern
This pattern forms a triangle shape using a repeated character or symbol.
Example:
Code
5. Diamond Character Pattern
This pattern forms a diamond shape using a repeated character or symbol.
Example:
Code
Conclusion
In this article, we explored various character patterns in Java, including right triangle alphabetic patterns, repeating alphabet patterns, K-shape alphabet patterns, triangle character patterns, and diamond character patterns. Each pattern demonstrated the use of nested loops, conditional statements, and character manipulation to achieve the desired output.
Character patterns are not only fun to create but also serve as great exercises for enhancing logical thinking, loop control, and string manipulation skills. By understanding the underlying principles and applying them creatively, you can generate an array of fascinating patterns using alphabets or any other printable characters available in Java.
FAQs
1. What is the process of creating a custom character pattern using special symbols or non-alphabetic characters in Java?
Indeed, Java offers the flexibility to use any printable character or symbol for the creation of custom character patterns. This can be achieved by leveraging the ASCII values of the characters or by directly using Unicode symbols to portray your desired pattern.
2. How can I develop a character pattern in Java that repeats a specific word or phrase instead of just a single character?
In order to craft a character pattern that replicates specific words or phrases, you would need to define a string variable and manipulate it within a loop structure. Through the usage of string concatenation or substring operations, you can attain the desired repetition and alignment in the pattern.
3. How is it possible to create animated character patterns in Java?
By employing advanced concepts such as multithreading, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), or external libraries like JavaFX, you can design dynamic character patterns that evolve over time, providing an animated visual effect.
-9cd0a42cab014b9e8d6d4c4ba3f27ab1.webp&w=3840&q=75)
Take the Free Quiz on Java
Answer quick questions and assess your Java knowledge


Author|900 articles published


upGrad Learner Support
Talk to our experts. We are available 7 days a week, 9 AM to 12 AM (midnight)
Indian Nationals
Foreign Nationals
Disclaimer
1.The above statistics depend on various factors and individual results may vary. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
2.The student assumes full responsibility for all expenses associated with visas, travel, & related costs. upGrad does not provide any a.